Mineral identificationPage
1
1
Slide 1
Section-2 Mineral Identification pg.68
Slide 2
What you’ll learn
Describe physical properties used to identify minerals.
Identify minerals using physical properties such as hardness and streak.
Slide 3
Physical Properties
Mineral appearance
Hardness
Luster
Specific gravity
Streak
Cleavage and fracture
Slide 4
Mineral appearance
How it looks like
What color is it?
Which one of the following is gold? Identify by appearance.
Slide 5
Hardness
A measure of how easily a mineral can be scratched
Slide 6
Properties of Minerals
Mohs Hardness Scale
Mineral
Talc
Gypsum
Calcite
Fluorite
Apatite
Feldspar
Quartz
Topaz
Corundum
Diamond
Rating
1 Softest known mineral. It flakes easily when scratched by a fingernail.
2 A fingernail can easily scratch it.
3 A fingernail cannot scratch it, but a copper penny can.
4 A steel knife can easily scratch it.
5 A steel knife can scratch it.
6 Cannot be scratched by a steel knife, but it can scratch window glass.
7 Can scratch steel and hard glass easily.
8 Can scratch quartz.
9 Can scratch topaz.
10 Hardest known mineral. Diamond can scratch all other substances.
Testing Method
Slide 7
Luster
The way a mineral reflects a light luster.
Either metallic or nonmetallic
Slide 8
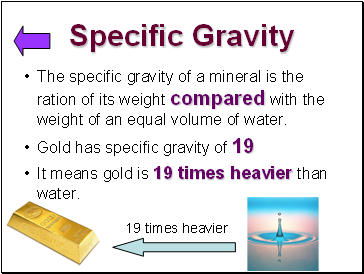
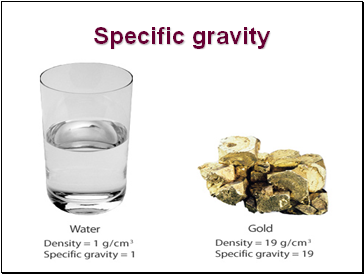
Specific Gravity
The specific gravity of a mineral is the ration of its weight compared with the weight of an equal volume of water.
Gold has specific gravity of 19
It means gold is 19 times heavier than water.
Slide 9
Specific gravity
Slide 10
Streak
When a mineral is rubbed across a piece of porcelain tile a streak of powdered mineral is left behind.
Slide 11
Cleavage
Cleavage is the way that mineral breaks.
Minerals that break along smooth, flat surfaces have cleavage.
Mica has cleavage
1 2
Contents
- Physical Properties
- Mineral appearance
- Hardness
- Properties of Minerals
- Luster
- Specific Gravity
- Streak
- Cleavage
- Fracture
Last added presentations
- Practical Applications of Solar Energy
- Sensory and Motor Mechanisms
- Magnetic field uses sound waves to ignite sun's ring of fire
- Newton's Laws
- Geophysical Concepts, Applications and Limitations
- Newton’s laws of motion
- History of Modern Astronomy