Societies to Social NetworksPage
1
1
Slide 1
Chapter Six:
Societies to Social Networks
www.sliderbase.com
Slide 2
www.sliderbase.com
“People who interact with one another and think of themselves as belonging together.”
What is a Group?
Slide 3
www.sliderbase.com
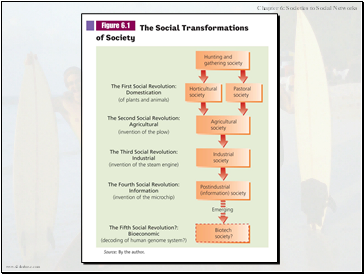
Domestication Revolution
Hunting and Gathering
Pastoral and Horticultural
Agricultural
Societies and Their Transformation
Slide 4
www.sliderbase.com
Industrial Revolution
Postindustrial (Information)
Bioeconomic—New Type?
Societies and Their Transformation
Slide 5
www.sliderbase.com
Slide 6
www.sliderbase.com
Slide 7
www.sliderbase.com
Not to be Confused with Groups .
Aggregate
Category
Groups Within Society
Slide 8
www.sliderbase.com
Primary Groups
Face-to-Face
The Family
Friends
Producing a Mirror Within
Groups Within Society
Slide 9
www.sliderbase.com
Secondary Groups
Larger, More Anonymous
Members Interact Based on Statuses
Fail to Satisfy Need for Intimate Association
Groups Within Society
Slide 10
www.sliderbase.com
In-Groups and Out-Groups
Loyalty to In-Groups
Antagonism Towards Out-Groups
Groups Within Society
Slide 11
www.sliderbase.com
In-Groups and Out-Groups Produce…
Loyalty
Sense of Superiority
Rivalries
Implications for Socially Diverse Society
Groups Within Society
Slide 12
www.sliderbase.com
Reference Groups
Provide a Yardstick
Expose Us to Contradictory Standards
Groups Within Society
Slide 13
www.sliderbase.com
Social Networks
The Small World Phenomenon
Is the Small World Phenomenon a Myth?
Groups Within Society
Slide 14
1 2
Contents
- What is a Group?
- Societies and Their Transformation
- Groups Within Society
- Group Dynamics
- Leadership
- Groupthink - Global Consequences
Last added presentations
- Buoyancy
- Space Radiation
- Ch 9 Nuclear Radiation
- Solar Energy
- Simulation at NASA for the Space Radiation Effort
- Resource Acquisition and Transport in Vascular Plants
- Upcoming Classes