Kinetic Molecular TheoryPage
1
1
Slide 1
Kinetic Molecular Theory
ki⋅net⋅ic
Origin: 1850Ė55; < Gk kīnētikós moving, equiv. to kīnē- (verbid s. of kīneîn to move) + -tikos
Source: Websters Dictionary
Slide 2
CA Standards
Slide 3
The Nature of Gases
Gases expand to fill their containers
Gases are fluid Ė they flow
Gases have low density
1/1000 the density of the equivalent liquid or solid
Gases are compressible
Gases effuse and diffuse
Slide 4
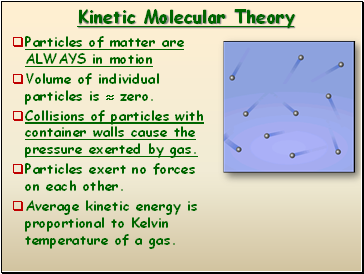
Kinetic Molecular Theory
Particles of matter are ALWAYS in motion
Volume of individual particles is zero.
Collisions of particles with container walls cause the pressure exerted by gas.
Particles exert no forces on each other.
Average kinetic energy is proportional to Kelvin temperature of a gas.
Slide 5
Kinetic Energy of Gas Particles
At the same conditions of temperature, all gases have the same average kinetic energy.
m = mass
v = velocity
At the same temperature, small molecules move FASTER than large molecules
Slide 6
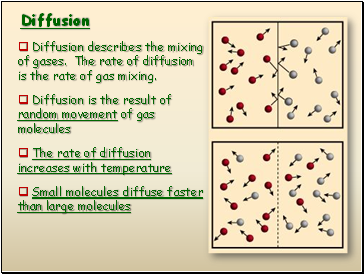
Diffusion
Diffusion describes the mixing of gases. The rate of diffusion is the rate of gas mixing.
Diffusion is the result of random movement of gas molecules
The rate of diffusion increases with temperature
Small molecules diffuse faster than large molecules
Slide 7
Grahamís Law of Diffusion
M1 = Molar Mass of gas 1
M2 = Molar Mass of gas 2
Slide 8
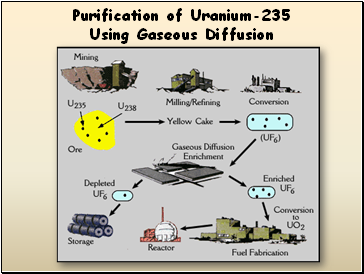
Purification of Uranium-235 Using Gaseous Diffusion
Contents
- Kinetic Molecular Theory
- The Nature of Gases
- Kinetic Molecular Theory
- Kinetic Energy of Gas Particles
- Diffusion
- Grahamís Law of Diffusion
Last added presentations
- Friction
- Radiation
- Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation
- Radioactivity and Nuclear Reactions
- Ch 9 Nuclear Radiation
- Solar Thermal Energy
- Motion