The Properties of Our SunPage
1
1
Slide 1
THE SUN
The star we see but seldom notice
Slide 2
Goals
Summarize the overall properties of the Sun.
What are the different parts of the Sun and how do we know this?
Where does the light we see come from?
Solar activity and magnetic fields.
Slide 3
The Sun, Our Star
The Sun is an average star.
From the Sun, we base our understanding of all stars in the Universe.
Like Jovian Planets it’s a giant ball of gas.
No solid surface.
Slide 4
Vital Statistics
Radius = 100 x Earth (696,000 km)
Mass = 300,000 x Earth (1.99 x 1030 kg)
Surface temp = 5780 K
Core temp = 15,000,000 K
Luminosity = 4 x 1026 Watts
Solar “Day” =
24.9 Earth days (equator)
29.8 Earth days (poles)
Slide 5
Structure
‘Surface’
Photosphere
‘Atmosphere’
Chromosphere
Transistion zone
Corona
Solar wind
‘Interior’
Convection zone
Radiation zone
Core
Slide 6
The Solar Interior
How do we know what’s inside the Sun?
Observe the outside.
Theorize what happens on the inside.
Complex computer programs model the theory.
Model predicts what will happen on the outside.
Compare model prediction with observations of the outside.
Scientific Method!
Slide 7
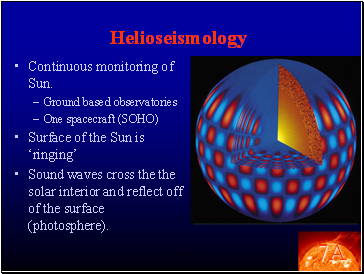
Helioseismology
Continuous monitoring of Sun.
Ground based observatories
One spacecraft (SOHO)
Surface of the Sun is ‘ringing’
Sound waves cross the the solar interior and reflect off of the surface (photosphere).
Slide 8
Interior Properties
Core = 20 x density of iron
Surface = 10,000 x less dense than air
Average density = Jupiter
Core = 15,000,000 K
Surface = 5780 K
Slide 9
Do you see the light?
Everything in the solar system reflects light.
Everything also absorbs light and heats up producing blackbody radiation.
Q: Where does this light come from?
A: The Sun.
But where does the Sun’s light come from?
Slide 10
Our Journey through the Sun
Contents
- Goals
- The Sun, Our Star
- Vital Statistics
- Structure
- The Solar Interior
- Helioseismology
- Interior Properties
- Do you see the light?
- Our Journey through the Sun
- In The Core
- Nuclear Fusion
- The Radiation Zone
- The Convection Zone
- Convection
- Solar Cross-Section
- The Photosphere
- The Solar Atmosphere
- Atmospheric Composition
- The Chromosphere
- Spicules and Prominences
- Prominences
- Corona
- Solar Wind
- The Aurora
- The Active Sun
- Solar Cycle
- Sunspots
- Magnetic fields and Sunspots
- Sunspot Numbers
- Active Regions
Last added presentations
- Health Physics
- History of Modern Astronomy
- Motion
- Newton’s third law of motion
- Radioactivity and Nuclear Reactions
- Practical Applications of Solar Energy
- Waves & Sound