Atomic Structure and Periodic TrendsPage
1
1
Slide 1
Atomic Structure and Periodic Trends
Slide 2
Atomic Structure and Periodic Trends
Lectures:
week1: W9 am; week2: W9 am (ICL) & 11 am (DP), F 9 am (DP); week 3: 9 am (ICL)
Books:
Inorganic Chemistry by Shriver and Atkins
Physical Chemistry by P.W.Atkins , J. De Paula
Essential Trends in Inorganic Chemistry D Mingos
Introduction to Quantum Theory and Atomic Structure
by P. A. Cox
Other resources:
Web-pages: http://timmel.chem.ox.ac.uk/lectures/
Ritchie/Titmuss, Quantum Theory of Atoms and Molecules, Hilary Term
Slide 3
Why study atomic electronic structure?
All of chemistry (+biochemistry etc.) ultimately boils down to molecular electronic structure.
Reason: electronic structure governs bonding and thus molecular structure and reactivity
Before it is possible to understand molecular electronic structure we need to introduce a number of concepts which are more easily demonstrated in atoms.
atomic structure molecular structure chemistry
Slide 4
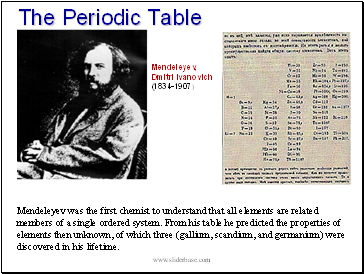
The Periodic Table
Mendeleyev was the first chemist to understand that all elements are related members of a single ordered system. From his table he predicted the properties of elements then unknown, of which three (gallium, scandium, and germanium) were discovered in his lifetime.
Mendeleyev,
Dmitri Ivanovich
(1834-1907)
Slide 5
This course
will introduce new concepts gradually starting with the “simplest”:
H-Atom Energy levels, Wavefunctions, Born Interpretation, Orbitals
Many electron atoms Effects of other electrons, Penetration, Quantum Defect
The Aufbau Principle Electronic Configuration of atoms and their ions
Trends in the PT Ionisation Energy, Electron Affinity, Size of atoms and ions
Slide 6
The H-Atom
H
1
1.008
Slide 7
The Hydrogen Atom
The simplest possible system and the basis for all others:
Electron orbits the proton
under the influence
of the Coulomb Force:
Revision
Slide 8
H-Atom: consider the energy
v
ETotal =
c.m.
Slide 9
Energy Levels?
Contents
- Atomic Structure and Periodic Trends
- Why study atomic electronic structure?
- The Periodic Table
- The Hydrogen Atom
- Energy Levels?
- The Rydberg Formula
- Bohr Theory (old quantum)
- The problem with Bohr Theory
- Quantum mechanical Principles and the Solution of the Schrödinger Equation
- The Results of Quantum Mechanics
- Spherical Polar Coordinates
- The quantum numbers;
- The Radial Wavefunctions
- Revisit: The Born Interpretation
- Radial Wavefunctions and the Born Interpretation
- The Surface area of a sphere is hence:
- Construction of the radial distribution function
- Radial distribution function P(r)
- The Angular Wavefunction
- The Shapes of Wavefunctions (Orbitals)
- Electron densities representations
- The energies of orbitals
- The Ionization Energy
- Other Atoms
- Periodic Trends
- Space for extra Notes
- More on Ionization Energies
- More Periodic Trends
- Appendices
Last added presentations
- Newton’s Laws of Motion
- Practical Applications of Solar Energy
- Heat-Energy on the Move
- Health Physics
- Magnetic field uses sound waves to ignite sun's ring of fire
- Space Radiation
- Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation