ADP, ATP and Cellular RespirationPage
1
1
Slide 1
ADP, ATP and Cellular Respiration
Slide 2
What Is ATP?
Energy used by all Cells
Adenosine Triphosphate
Organic molecule containing high-energy Phosphate bonds
Slide 3
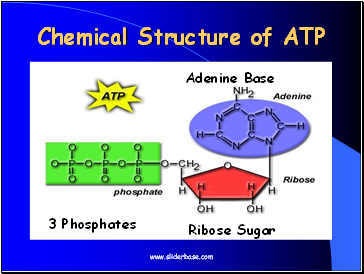
Chemical Structure of ATP
3 Phosphates
Ribose Sugar
Adenine Base
Slide 4
What Does ATP Do for You?
It supplies YOU with ENERGY!
Slide 5
How Do We Get Energy From ATP?
By breaking the high- energy bonds between the last two phosphates in ATP
Slide 6
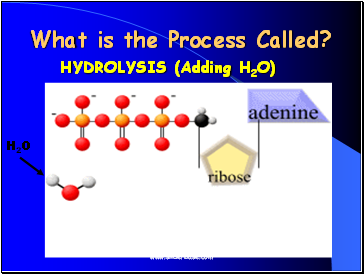
What is the Process Called?
HYDROLYSIS (Adding H2O)
H2O
Slide 7
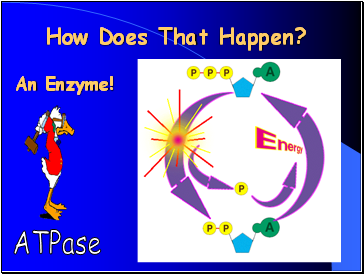
How Does That Happen?
ATPase
An Enzyme!
Slide 8
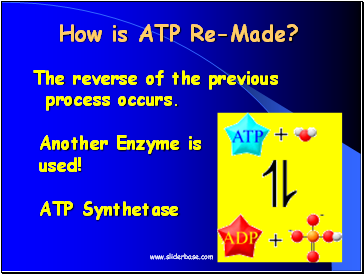
How is ATP Re-Made?
The reverse of the previous process occurs.
Another Enzyme is used!
ATP Synthetase
Slide 9
The ADP-ATP Cycle
ATP-ase
ATP Synthetase
Slide 10
When is ATP Made in the Body?
During a Process called Cellular Respiration that takes place in both Plants & Animals
Slide 11
Cellular Respiration
Includes pathways that require oxygen
Glucose is oxidized and O2 is reduced
Glucose breakdown is therefore an oxidation-reduction reaction
Breakdown of one glucose results in 36 to 38 ATP molecules
Slide 12
Overall Equation for Cellular Respiration
6CO2 + 6H20 + e- + 36-38ATPís
C6H12O6 + 6O2
YIELDS
Slide 13
What Type of Process is Cellular Respiration?
An Oxidation-Reduction Process or REDOX Reaction
Oxidation of GLUCOSE --> CO2 + H2O (e- removed from C6H12O6)
Reduction O2 to H2O (e- passed to O2)
Slide 14
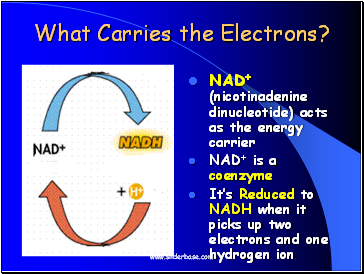
What Carries the Electrons?
NAD+ (nicotinadenine dinucleotide) acts as the energy carrier
NAD+ is a coenzyme
Itís Reduced to NADH when it picks up two electrons and one hydrogen ion
Contents
- What Is ATP?
- What Does ATP Do for You?
- The ADP-ATP Cycle
- Cellular Respiration
- Diagram of the Process
- Glycolysis Summary
- Fermentation
- Krebs Cycle Summary
Last added presentations
- Ch 9 Nuclear Radiation
- Radiation
- Newton's laws of motion
- Friction
- Gravitation
- Geophysical Concepts, Applications and Limitations
- Resource Acquisition and Transport in Vascular Plants