Reduction-DivisionPage
1
1
Slide 1
MEIOSIS
Reduction-Division
Genetic Recombination
Slide 2
Meiosis
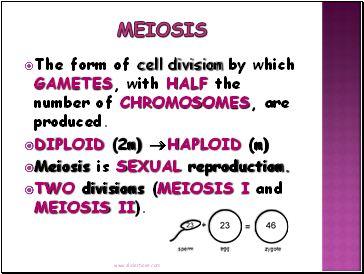
The form of cell division by which GAMETES, with HALF the number of CHROMOSOMES, are produced.
DIPLOID (2n) HAPLOID (n)
Meiosis is SEXUAL reproduction.
TWO divisions (MEIOSIS I and MEIOSIS II).
Slide 3
Meiosis
Sex cells divide to produce GAMETES (sperm or egg).
Gametes have HALF the # of chromosomes.
Occurs only in GONADS (testes or ovaries).
Male: SPERMATOGENESIS -sperm
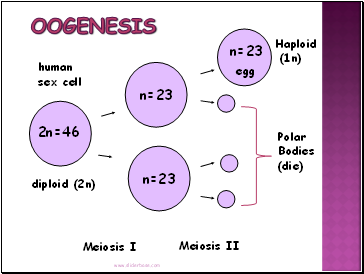
Female: OOGENESIS - egg or ova
Slide 4
Spermatogenesis
Slide 5
Oogenesis
Polar Bodies (die)
Slide 6
Interphase I
Similar to mitosis interphase.
CHROMOSOMES (DNA) replicate in the S phase
Each duplicated chromosome consist of two identical SISTER CHROMATIDS attached at their CENTROMERES.
CENTRIOLE pairs also replicate.
Slide 7
Interphase I
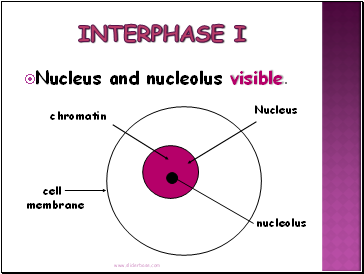
Nucleus and nucleolus visible.
Nucleus
nucleolus
cell membrane
chromatin
Slide 8
Meiosis I (four phases)
Cell division that reduces the chromosome number by one-half.
Four phases:
a. Prophase I
b. Metaphase I
c. Anaphase I
d. Telophase I
Prophase I
Slide 9
Prophase I
Longest and most complex phase (90%).
Chromosomes condense.
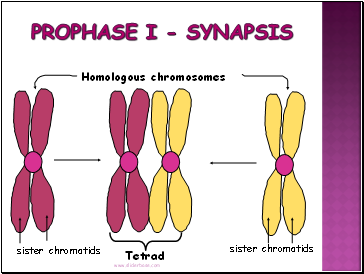
Synapsis occurs - Homologous chromosomes come together to form a tetrad.
Tetrad is two chromosomes or four chromatids (sister and non-sister chromatids).
Slide 10
Non-Sister Chromatids-HOMOLOGS
Homologs contain DNA that codes for the same genes , but different versions of those genes
Genes occur at the same loci
Slide 11
Prophase I - Synapsis
Slide 12
Homologous Chromosomes
Pair of chromosomes (maternal and paternal) that are similar in shape and size.
Homologous pairs (tetrads) carry GENES controlling the SAME inherited traits.
Contents
- Meiosis
- Spermatogenesis
- Oogenesis
- Interphase I
- Prophase I
- Non-Sister Chromatids-HOMOLOGS
- Homologous Chromosomes
- Crossing Over
- Sex Chromosomes
- Variation
- Karyotype
- Fertilization
Last added presentations
- Static and Kinetic Friction
- Waves & Sound
- Madame Marie Curie
- Simulation at NASA for the Space Radiation Effort
- Newton’s Laws of Motion
- History of Modern Astronomy
- Sensory and Motor Mechanisms