Cellular respirationPage
1
1
Slide 1
Cellular Respiration
Slide 2
Cellular Respiration
A catabolic, exergonic, oxygen (O2) requiring process that uses energy extracted from macromolecules (glucose) to produce energy (ATP) and water (H2O).
C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy
Slide 3
Question:
In what kinds organisms does cellular respiration take place?
Slide 4
Plants and Animals
Plants - Autotrophs: self-producers.
Animals - Heterotrophs: consumers.
Slide 5
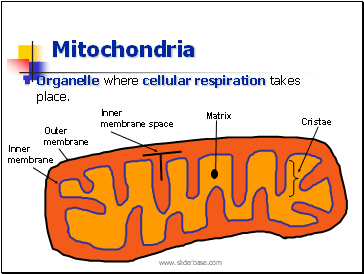
Mitochondria
Organelle where cellular respiration takes place.
Slide 6
Redox Reaction
Transfer of one or more electrons from one reactant to another.
Two types:
1. Oxidation
2. Reduction
Slide 7
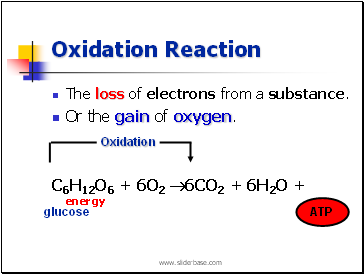
Oxidation Reaction
The loss of electrons from a substance.
Or the gain of oxygen.
C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy
Slide 8
Reduction Reaction
The gain of electrons to a substance.
Or the loss of oxygen.
Slide 9
Breakdown of Cellular Respiration
Four main parts (reactions).
1. Glycolysis (splitting of sugar)
a. cytosol, just outside of mitochondria.
2. Grooming Phase
a. migration from cytosol to matrix.
Slide 10
Breakdown of Cellular Respiration
3. Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle)
a. mitochondrial matrix
4. Electron Transport Chain (ETC) and
Oxidative Phosphorylation
a. Also called Chemiosmosis
b. inner mitochondrial membrane.
Slide 11
1. Glycolysis
Occurs in the cytosol just outside of mitochondria.
Two phases (10 steps):
A. Energy investment phase
a. Preparatory phase (first 5 steps).
B. Energy yielding phase
a. Energy payoff phase (second 5 steps).
Slide 12
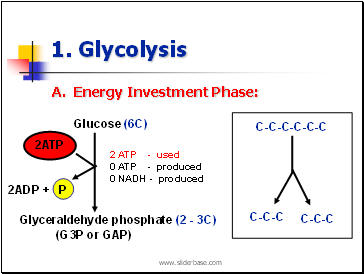
1. Glycolysis
A. Energy Investment Phase:
Slide 13
Contents
- Substrate-Level Phosphorylation
- Fermentation
- Alcohol Fermentation
- Lactic Acid Fermentation
- Cellular Respiration
- Plants and Animals
- Mitochondria
- Redox Reaction
- Oxidation Reaction
- Reduction Reaction
- Breakdown of Cellular Respiration
- Prokaryotes (Lack Membranes)
- Catabolism of Various Food Molecules
Last added presentations
- Radiation
- Solar Energy
- Buoyancy
- Mechanical, Electromagnetic, Electrical, Chemical and Thermal
- Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation
- Simulation at NASA for the Space Radiation Effort
- Direct heat utilization of geothermal energy