Nucleic AcidsPage
1
1
Slide 1
Nucleic Acids
DNA & RNA
Slide 2
What are they ?
The 4th type of macromolecules
The chemical link between generations
The source of genetic information in chromosomes
Slide 3
What do they do ?
Dictate amino-acid sequence in proteins
Give information to chromosomes, which is then passed from parent to offspring
Slide 4
What are they made of ?
Simple units called nucleotides, connected in long chains
Nucleotides have 3 parts:
1- 5-Carbon sugar (pentose)
2- Nitrogen containing base
(made of C, H and N)
3- A phosphate group ( P )
The P groups make the links that unite the sugars (hence a “sugar-phosphate backbone”
Slide 5
Two types of Nucleotides (depending on the sugar they contain)
1- Ribonucleic acids (RNA)
The pentose sugar is Ribose (has a hydroxyl group in the 3rd carbon---OH)
2- Deoxyribonucleic acids (DNA)
The pentose sugar is Deoxyribose (has just an hydrogen in the same place--- H) Deoxy = “minus oxygen”
Slide 6
DNA Nucleotides Composition (3 parts):
1- Deoxyribose sugar (no O in 3rd carbon)
2- Phosphate group
3- One of 4 types of bases (all containing nitrogen):
- Adenine
- Thymine (Only in DNA)
- Cytosine
- Guanine
Slide 7
RNA Nucleotides Composition ( 3 parts):
1- Ribose sugar (with O in 3rd carbon)
2- Phosphate group
3- One of 4 types of bases (all containing nitrogen):
- Adenine
- Uracyl (only in RNA)
- Cytosine
- Guanine
Slide 8
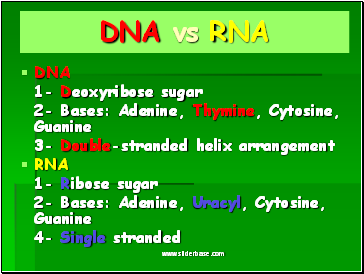
DNA vs RNA
DNA
1- Deoxyribose sugar
2- Bases: Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine
3- Double-stranded helix arrangement
RNA
1- Ribose sugar
2- Bases: Adenine, Uracyl, Cytosine, Guanine
4- Single stranded
Slide 9
The Double Helix (DNA) Structural model:
Model proposed by Watson & Crick, 1953
Two sugar-phosphate strands, next to each other, but running in opposite directions.
Specific Hydrogen bonds occur among bases from one chain to the other:
A---T , C---G
Due to this specificity, a certain base on one strand indicates a certain base in the other.
1 2
Contents
- What are they ?
- What do they do ?
- What are they made of ?
- Two types of Nucleotides (depending on the sugar they contain)
- How DNA Works
Last added presentations
- Geophysical Concepts, Applications and Limitations
- Radioactivity and Nuclear Reactions
- Motion
- Thermal Energy
- Newton’s third law of motion
- Space Radiation
- Upcoming Classes