Viruses and HIVPage
1
1
Slide 1
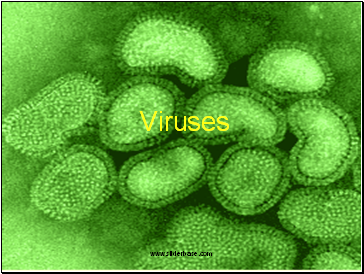
Viruses
Slide 2
Is a Virus a Living Organism?
Chapter 1 – Properties of life
Cellular Respiration
Reproduction
Metabolism
Homeostasis
Heredity
Responsiveness
Growth and development
Slide 3
Viruses are not living organisms
Viruses do not
Grow
Have homeostasis
Metabolize
Viruses do
Infect cells and use the cell to make more viruses
Cause disease in many organisms
Slide 4
Parts of a Virion (a virus particle)
Nucleic Acid – RNA or DNA
Capsid – protein coat that surrounds the DNA or RNA in a virus
Lipid Membrane – a membrane around the capsid in many kinds of viruses; helps the virus enter cells (“enveloped” viruses; without the membrane, the virus is “naked”)
Made of proteins, lipids, and glycoproteins
Slide 5
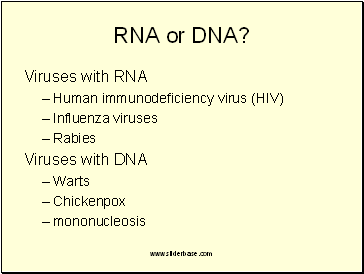
RNA or DNA?
Viruses with RNA
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
Influenza viruses
Rabies
Viruses with DNA
Warts
Chickenpox
mononucleosis
Slide 6
Virus Shapes
Helical
Rodlike with capsid proteins winding around the core in a spiral
Tobacco Mosaic Virus
Slide 7
Virus Shapes
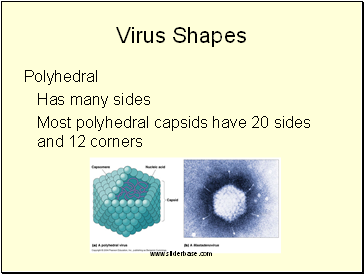
Polyhedral
Has many sides
Most polyhedral capsids have 20 sides and 12 corners
Slide 8
Virus Shapes
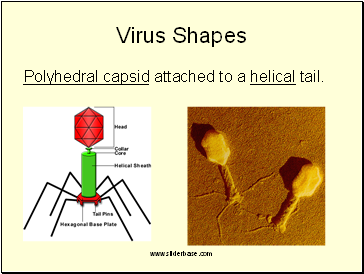
Polyhedral capsid attached to a helical tail.
Slide 9
How do viruses replicate?
2 methods of replication:
1. Lytic Cycle – the virus enters the cell, replicates itself hundreds of times, and then bursts out of the cell, destroying it.
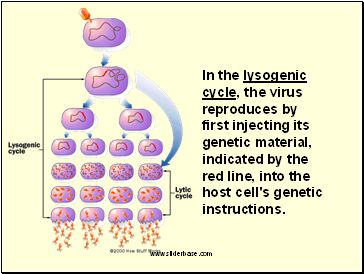
2. Lysogenic Cycle – the virus DNA integrates with the host DNA and the host’s cell helps create more virus DNA. An environmental change may cause the virus to enter the Lytic Cycle.
Slide 10
In the lytic cycle, the virus reproduces itself using the host cell's chemical machinery. The red spiral lines in the drawing indicate the virus's genetic material. The orange portion is the outer shell that protects it.
Slide 11
Contents
- Viruses
- Is a Virus a Living Organism?
- Viruses are not living organisms
- Parts of a Virion (a virus particle)
- RNA or DNA?
- Virus Shapes
- Viruses Enter Living Cells
- Mutating viruses
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS)
- Basic Structure
- DNA enters nucleus & binds with host DNA
Last added presentations
- Solar Energy
- Friction
- Sound
- History of Modern Astronomy
- Static and Kinetic Friction
- Newton's laws of motion
- Mechanical, Electromagnetic, Electrical, Chemical and Thermal