HormonesPage
1
1
Slide 1
Gametes
Gametes… of the sexes
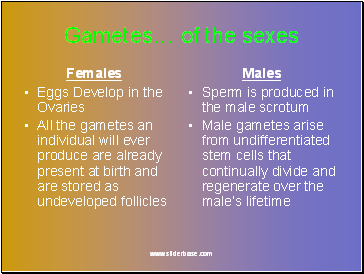
Females
Eggs Develop in the Ovaries
All the gametes an individual will ever produce are already present at birth and are stored as undeveloped follicles
Males
Sperm is produced in the male scrotum
Male gametes arise from undifferentiated stem cells that continually divide and regenerate over the male’s lifetime
Slide 2
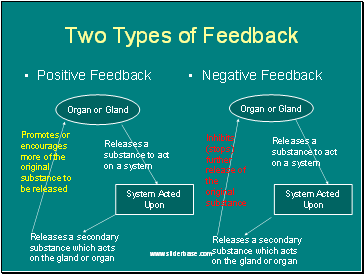
Two Types of Feedback
Positive Feedback
Negative Feedback
Organ or Gland
Organ or Gland
Releases a substance to act on a system
Releases a substance to act on a system
System Acted
Upon
System Acted
Upon
Releases a secondary substance which acts on the gland or organ
Releases a secondary substance which acts on the gland or organ
Inhibits (stops) further release of the original substance
Promotes or encourages more of the original substance to be released
Slide 3
Three Primary Hormones of Sexual Development
Estrogen
Progesterone
Testosterone
Slide 4
Estrogen’s Effects on Female Sexual Development
Works with Progesterone through “Feedback Loops” to establish regular reproductive cycles
Growth and Maturation of Female Sex Organs
During Puberty, triggers lengthening of long bones, and changes in pelvic structure
Slide 5
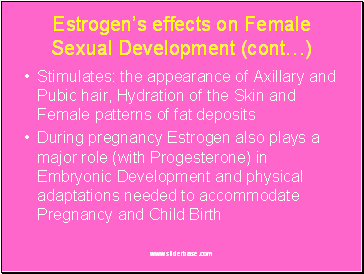
Estrogen’s effects on Female Sexual Development (cont…)
Stimulates: the appearance of Axillary and Pubic hair, Hydration of the Skin and Female patterns of fat deposits
During pregnancy Estrogen also plays a major role (with Progesterone) in Embryonic Development and physical adaptations needed to accommodate Pregnancy and Child Birth
Slide 6
Testosterone’s Effects on Male Sexual Development
Growth and Maturation of Male Sex Organs, Must be held at Adequate levels to maintain functioning of Male Sex Organs
At puberty stimulates the growth of axillary, pubic, facial and chest hair.
Enlargement of Larynx (deepening voice)
Slide 7
Testosterone’s Effects on Male Sexual Development (cont…)
Thickens Skin and Increases Oiliness
Enhances Growth and Density of Bones
Increases Muscles in Size and Mass
Boosts the Basal Metabolic Rate and Influences Behavior (Sex Drive)
“Masculinizes” the Brain (Promotes Aggressiveness)
Slide 8
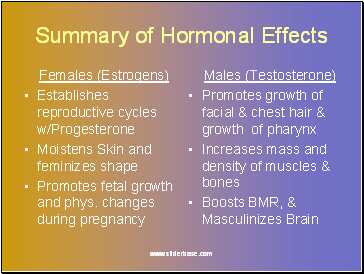
Summary of Hormonal Effects
1 2
Contents
- Gametes
- Two Types of Feedback
- Three Primary Hormones of Sexual Development
- Testosterone’s Effects on Male Sexual Development
- Summary of Hormonal Effects
- Effects common to both sexes
Last added presentations
- Upcoming Classes
- Sound
- Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation
- Newton’s law of universal gravitation
- Newton's laws of motion
- Radiation Safety and Operations
- Solar Energy