Being HealthyPage
1
1
Slide 1
Being Healthy
Breathing and the lungs
Slide 2
Objectives & Outcomes
Objective: Develop understanding of the structure of the lungs and gas exchange.
Outcomes:
All: Explain the process of breathing (4)
Most: Describe the difference between inhaled and exhaled air (5)
Some: Describe how alveoli are adapted for their purpose (6/7)
Extension: Describe how damaged alveoli can result in less gas exchange (7)
Slide 3
The Respiratory System
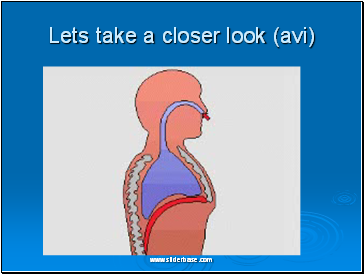
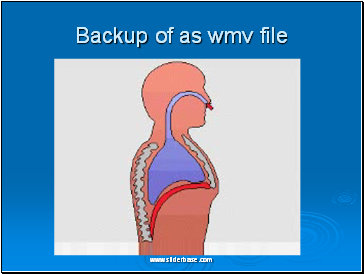
Gas exchange happens in the lungs.
You have 2 lungs, situated in your upper thorax / chest
Here, oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged – oxygen is needed for life and carbon dioxide is got rid of when we breathe out.
Slide 4
How do we breathe?
Mouth
Windpipe/trachea
bronchi
bronchioles
alveoli
blood
Slide 5
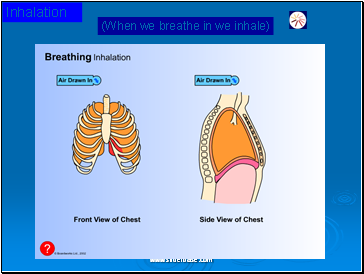
Inhalation
(When we breathe in we inhale)
Slide 6
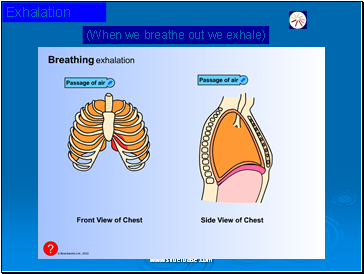
Exhalation
(When we breathe out we exhale)
Slide 7
Exchanging gases
Slide 8
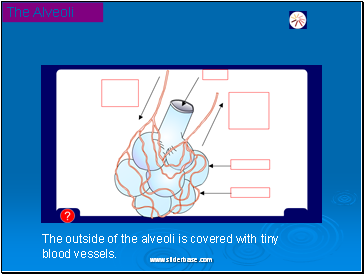
The Alveoli
The outside of the alveoli is covered with tiny blood vessels.
Oxygen makes its way into thousands of special air sacs collectively called the ALVEOLI.
Slide 9
The Alveolus
One of these alveoli is called the ALVEOLUS.
This is where the oxygen is transferred into the blood and carbon dioxide moves out of the blood.
If all these alveoli flattened and spread out onto the floor, they would cover an area the size of a tennis court!
Slide 10
Comparing inhaled and exhaled air
What are the big differences between inhaled and exhaled air?
How could you test for these?
There is another difference……
…… water vapour.
Slide 11
Lets take a closer look (avi)
Slide 12
Backup of as wmv file
Slide 13
1 2
Contents
- Breathing and the lungs
- Objectives & Outcomes
- The Respiratory System
- How do we breathe?
- Exchanging gases
- The Alveoli
- Backup of as wmv file
- Plenary
Last added presentations
- Solar Energy
- Sound
- Radioactivity and Nuclear Reactions
- Newton’s law of universal gravitation
- Newton’s laws of motion
- Magnetic field uses sound waves to ignite sun's ring of fire
- Gravitation