Plant structure adaptations and responsesPage
1
1
Slide 1
Structure of Plants
Slide 1
Slide 2
A. Functions of Roots
Anchor & support plant in the ground
Absorb water & minerals
Hold soil in place
Slide 2
Fibrous Roots
Root Hairs
Slide 3
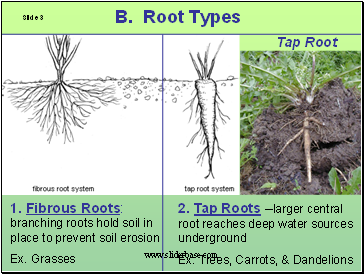
B. Root Types
2. Tap Roots –larger central root reaches deep water sources underground
Ex. Trees, Carrots, & Dandelions
1. Fibrous Roots: branching roots hold soil in place to prevent soil erosion
Ex. Grasses
Slide 3
Tap Root
Slide 4
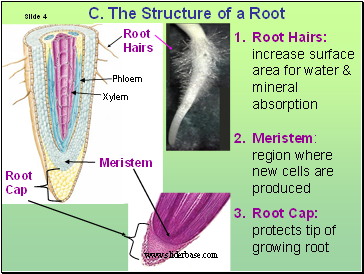
Root Hairs: increase surface area for water & mineral absorption
Meristem: region where new cells are produced
Root Cap: protects tip of growing root
C. The Structure of a Root
Slide 4
Root Hairs
Meristem
Root Cap
Xylem
Phloem
Slide 5
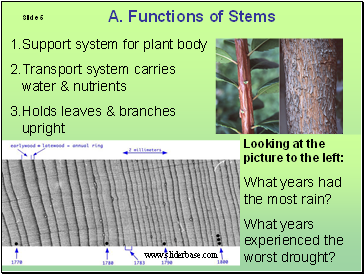
Functions of Stems
Support system for plant body
Transport system carries water & nutrients
Holds leaves & branches upright
Slide 5
Each light and dark tree ring equals one year of annual growth. Light rings for fast spring growth, dark for slow summer growth.
Smaller rings tell of past droughts that have occurred.
Looking at the picture to the left:
What years had the most rain?
What years experienced the worst drought?
Slide 6
Functions of Leaves
Slide # 6
Main photosynthetic organ
Broad, flat surface increases surface area for light absorption
Have systems to prevent water loss
Stomata open in day but close at night or when hot to conserve water
waxy cuticle on surface
System of gas exchange
Allow CO2 in and O2 out of leaf
Elephant Ear Plant
Slide 7
Leaf Structures
Cuticle: waxy layer; covers upper surface
Protects leaf against water loss
Veins: transports water, nutrients and food
Made of xylem and phloem
Mesophyll: contains cells that perform photosynthesis
b/c they contain Chloroplasts.
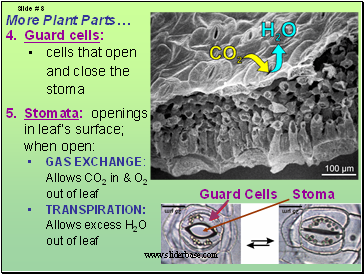
2 Guard Cells
Surround
each
Stoma
Mesophyll
Slide # 7
(Opening)
Leaf Cross-Section
Veins
Cuticle
Stoma
Stoma- singular
Stomata-plural
Slide 8
More Plant Parts…
Guard Cells
Guard cells:
cells that open and close the stoma
Stomata: openings in leaf’s surface; when open:
Contents
- Structure of Plants
- Functions of Stems
- Functions of Leaves
- Leaf Structures
- Stoma Open
- Plants find a use for Transpiration
- Structure of a Flower
- Cross Pollination
- Responses and Adaptations
- Hormone-producing cells
- Ethylene causes Fruit to Ripen
- Plant Tropisms
- What type of tropism is shown in these pictures?
Last added presentations
- Radioactivity and Nuclear Reactions
- Buoyancy
- Newton’s law of universal gravitation
- Practical Applications of Solar Energy
- Geophysical Concepts, Applications and Limitations
- Heat-Energy on the Move
- History of Modern Astronomy