Genetic TestingPage
1
1
Slide 1
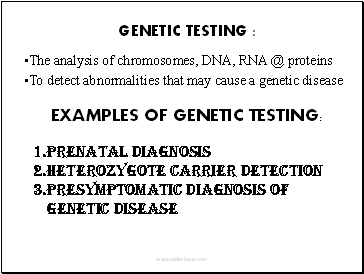
GENETIC TESTING :
The analysis of chromosomes, DNA, RNA @ proteins
To detect abnormalities that may cause a genetic disease
EXAMPLES OF GENETIC TESTING:
PRENATAL DIAGNOSIS
HETEROZYGOTE CARRIER DETECTION
PRESYMPTOMATIC DIAGNOSIS OF GENETIC DISEASE
Slide 2
Screening Tests
Aimed at identifying a subset of the population on whom further.
DIAGNOSTIC TEST
Are not intended to provide definitive diagnoses.
Designed to detect treatable human diseases in their presymptomatic stage.
Slide 3
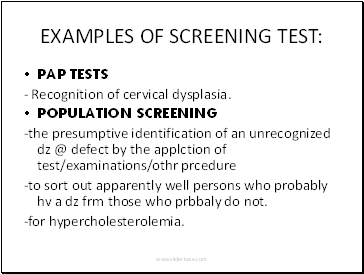
Examples Of Screening Test
PAP TESTS
- Recognition of cervical dysplasia.
POPULATION SCREENING
-the presumptive identification of an unrecognized dz @ defect by the applction of test/examinations/othr prcedure
-to sort out apparently well persons who probably hv a dz frm those who prbbaly do not.
-for hypercholesterolemia.
Slide 4
Principles Of Screening
Slide 5
Genetic Screening
Slide 6
What is genetic screening?
One of the fastest moving fields in medical science.
A technique to determine the genotype or phenotype of an organism.
It is often used to detect faulty or abnormal genes in an organism.
Slide 7
TYPES OF GENETIC SCREENING:
Newborn Screening
-for inherited metabolic diseases
2. Heterozygote Screening
-for Tay-Sachs disease
Slide 8
Newborn Screening
Newborns are tested for diseases and early diagnoses allows for immediate treatment (early detection &effective intervention).
A blood sample is tested for genetic disorders.
An effective public health strategy for treatable disorder such as PKU, galactosemia, hypothyroidism
& sickle cell disease.
Some communities begun screening for Duschenne muscular dystrophy (by measuring creatine kinase levels in newborns)
Slide 9
Heterozygote Screening
To detect unaffected carriers of disease-causing mutations
Target population: group known to be at risk.
Usually genetic diseases involves in this heterozygote screening is “autosomal recessive disorder”- Tay-Sachs disease, -Thalassemia & Cystic fibrosis.
1 2
Contents
- Screening Tests
- Examples Of Screening Test
- Principles Of Screening
- Genetic Screening
- What is genetic screening?
- Newborn Screening
- Heterozygote Screening
- Presymptomatic Diagnosis
- Advantage of Presymptomatic Diagnosis
Last added presentations
- Practical Applications of Solar Energy
- Newton's laws of motion
- Sound
- Buoyancy
- Gravitation
- Sound
- Newton’s law of universal gravitation