WavesPage
1
1
Slide 1
Waves: sound & light
Waves carry energy from one place to another
© 2000 Microsoft Clip Gallery
Slide 2
Nature of waves
Waves (Def.) A wave is a disturbance that transfers energy.
Medium Substance or region through which a wave is transmitted.
Speed of Waves Depends on the properties of the medium.
© 2000 Microsoft Clip Gallery
Slide 3
SAMPLE LESSON: Light & the Electromagnetic Spectrum
By D. L. Power
Revised 1/20/01
© 2000 Microsoft Clip Gallery
Slide 4
Albert Einstein
Slide 5
Light: What Is It?
Light Energy
Atoms
As atoms absorb energy, electrons jump out to a higher energy level.
Electrons release light when falling down to the lower energy level.
Photons - bundles/packets of energy released when the electrons fall.
Light: Stream of Photons
© 2000 Microsoft Clip Gallery
© 2000 Microsoft Clip Gallery
Slide 6
Electromagnetic Waves
Speed in Vacuum
300,000 km/sec
186,000 mi/sec
Speed in Other Materials
Slower in Air, Water, Glass
© 2000 Microsoft Clip Gallery
Slide 7
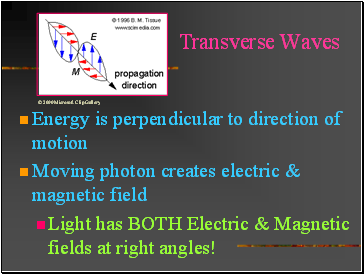
Transverse Waves
Energy is perpendicular to direction of motion
Moving photon creates electric & magnetic field
Light has BOTH Electric & Magnetic fields at right angles!
© 2000 Microsoft Clip Gallery
Slide 8
Electromagnetic Spectrum
© 2000 Microsoft Clip Gallery
Slide 9
Electromagnetic Spectrum
Visible Spectrum Light we can see
Roy G. Biv Acronym for Red, Orange, Yellow, Green, Blue, Indigo, & Violet.
Largest to Smallest Wavelength.
Slide 10
Electromagnetic Spectrum
Invisible Spectrum
Radio Waves
Def. Longest wavelength & lowest frequency.
Uses Radio & T.V. broadcasting.
© 2000 Microsoft Clip Gallery
Slide 11
Modulating Radio Waves
Modulation - variation of amplitude or frequency when waves are broadcast
AM amplitude modulation
Contents
- Waves: sound & light
- Nature of waves
- Light: What Is It?
- Electromagnetic Waves
- Transverse Waves
- Electromagnetic Spectrum
- Modulating Radio Waves
- Short Wavelength Microwave
- Light: Particles or Waves?
- Light: Refraction of Light
- Color of Light
- How You See
- Paint Pigments
- Complementary Pigments
- Light & its uses
- How You See
- Light & uses: Lenses
- Light & uses: Optical Instruments
- Light & uses: Diffraction
- Evaluation: State Standards
Last added presentations
- Radioactivity and Nuclear Reactions
- The Effects of Radiation on Living Things
- Newtons law of universal gravitation
- Magnetic field uses sound waves to ignite sun's ring of fire
- Solar Energy
- Waves & Sound
- Mechanical, Electromagnetic, Electrical, Chemical and Thermal