Gravity and Circular Motion RevisionPage
1
1
Slide 1
Gravity and Circular Motion Revision AQA syllabus A Section 13.3.1-6
B.W.Hughes
Slide 2
Circular motion
When an object undergoes circular motion it must experience a
centripetal force
This produces an acceleration
towards the centre of the circle
Slide 3
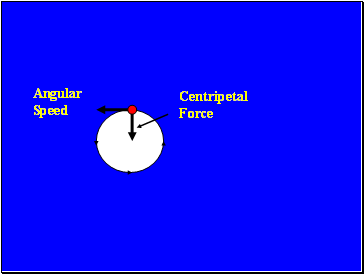
Angular Speed
Centripetal Force
Slide 4
Slide 5
Slide 6
Slide 7
Angular speed
Angular speed can be measured in ms-1 or
Rads-1 (radians per second) or
Revs-1 (revolutions per second)
The symbol for angular speed in radians per second is
ω
Slide 8
Converting to ω
To convert v to ω
ω = v/r
To convert revs per second to ω
Multiply by 2π
Slide 9
Acceleration
The acceleration towards the centre of the circle is
a = v2/r OR
a = ω2r
Slide 10
Centripetal Force Equation
The general force equation is
F = ma
so the centripetal force equation is
F = mv2/r OR
F = m ω2r
THESE EQUATIONS MUST BE LEARNED!!
Slide 11
Example
Gravity provides the accelerating force to keep objects in contact with a humpback bridge. What is the minimum radius of a bridge that a wheel will stay in contact with the road at 10 ms-1?
v = 10 ms-1, g = 10 ms-2, r = ?
a = v2/r = g so r = v2/g
r = 102/10 = 10 m
Slide 12
Newton’s Gravitation Equation
Newton’s Gravitation equation is
F = -Gm1m2/r2
MUST BE LEARNED!!
Negative sign is
a vector sign
G is
Universal Gravitational Constant
Slide 13
More about the equation
m1 and m2 are
the two gravitating masses
r is
the distance between their centres of gravity
The equation is an example of an
Inverse square law
Slide 14
Contents
- Circular motion
- Angular speed
- Converting to ω
- Centripetal Force Equation
- Example
- Newton’s Gravitation Equation
- More about the equation
- Gravitational field
- Radial Field
- Gravitational Potential
- Potential Gradient
- Field strength graph notes
- Potential Graph Notes
- Orbits
- More orbital mechanics
- Example
Last added presentations
- Motion
- Radiation
- Radioactivity and Nuclear Reactions
- Simulation at NASA for the Space Radiation Effort
- Newton’s Law of Gravity
- Heat-Energy on the Move
- Newton’s Laws of Motion