AccelerationPage
1
1
Slide 1
Acceleration
Graphs and Problems
Slide 2
a. A car is moving eastward along Lake Avenue and increasing its speed from 25 mph to 45 mph.
b. A northbound car skids to a stop to avoid a reckless driver.
c. An Olympic diver slows down after splashing into the water.
d. A southward-bound free kick delivered by the opposing team is slowed down and stopped by the goalie.
e. A downward falling parachutist pulls the chord and rapidly slows down.
f. A rightward-moving Hot Wheels car slows to a stop.
g. A falling bungee-jumper slows down as she nears the concrete sidewalk below
For each sentence determine the direction of acceleration.
As a general rule
if object is increasing speed acceleration is in the same direction as motion
if object is slowing down acceleration is in the opposite direction
Slide 3
Representing acceleration graphically
Describe the motion indicated by the graphs.
Slide 4
Examples - calculating Acceleration
The velocity of the aircraft is reduced from 100 m/s[S] to 40 m/s[S] in 8 s. Find itís average acceleration.
Slide 5
example 2
A truck is moving east at a speed of 20 m/s. The driver presses on the gas pedal and truck accelerates at the rate of 1.5 m/s2 [E] for 7 seconds. What is the final velocity of the truck?
Slide 6
example 3
A truck is moving east at a speed of 30 m/s. The driver presses on the brake pedal and truck accelerates at the rate of 4.5 m/s2 [W] for 5 seconds. What is the final velocity of the truck?
Slide 7
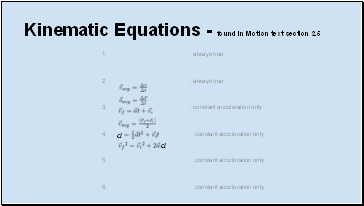
Kinematic Equations - found in Motion text section 2.5
, always true
, always true
, constant acceleration only
, constant acceleration only
, constant acceleration only
, constant acceleration only
d
d
Slide 8
example 4- finding average velocity
A motorcycle accelerates uniformly from +40 ft/s to +120 ft/s in 7 seconds. Find the average velocity
use vavg - ½(vi + vf). this only works if acceleration is constant and uniform.
Slide 9
example 5
A car is moving at +25 m/s. It then accelerates at a rate of 1.5 m/s2 for 10 s. Find itís final velocity.
1 2
Contents
Last added presentations
- Newtonís Laws of Motion
- Solar Energy
- Radiation Safety and Operations
- Practical Applications of Solar Energy
- Space Radiation
- Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation
- Motion