Chemical Bonding revisedPage
1
1
Slide 1
Unit 2: Bonding
Slide 2
Overview
Covalent Bonding
Ionic and Metallic Bonding
Electronegativity
Molecular Shape
Polarity
Ionic Crystals
Network Solids
Intermolecular Forces
Slide 3
Covalent Bonding
Bonds between atoms are formed through the sharing of electrons
Covalent bonds form between two non-metal atoms through sharing of pairs of electrons
Atoms have a “desire” to have their outer energy levels filled (Octet Rule)
Covalent bonding can be represented with Lewis Dot Diagrams
Slide 4
Lewis Dot Diagrams
Lewis Dot Diagrams show the sharing of electrons between atoms and where the bonds form
atoms share electrons to fill their outer energy levels (8 electrons in their outer shell)
The exception is hydrogen (2 electrons in its outer shell)
Slide 5
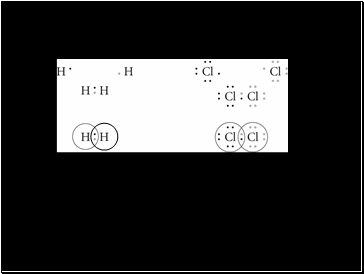
Lewis Dot Diagrams for Hydrogen and Chlorine Gas
The first row shows the atoms before they are bonded
The second row shows the sharing of electrons to fill the outer energy level
The third row has circles around the electrons to show those that belong to each atom. Where the circles overlap represents a covalent bond
Slide 6
Multiple Bonds
Double and triple bonds can form between atoms in order to fill the outer energy level
This occurs when two atoms share more than one pair of electrons
Slide 7
Multiple Lewis Structures
Some molecules can have more than one possible Lewis structure, usually when one single bond and one double bond can be exchanged within the rules of drawing Lewis structures
Example of SO2 (g)
Slide 8
Structural Diagrams
Lewis Diagrams can be converted to structural diagrams for convenience
Structural diagrams use lines to represent a bond, or a pair of electrons, but it does not show lone electron pairs
Example: Chlorine Gas
Slide 9
Lewis Dot Diagram Worksheet
Using the rules for drawing Lewis dot diagrams, complete the worksheet (LDD and structural)
For extra practice, try the Lewis Structures Thought Lab
Slide 10
Stereochemistry – The Structures of Molecular Compounds
Contents
- Covalent Bonding
- Lewis Dot Diagrams
- Multiple Bonds
- Multiple Lewis Structures
- Structural Diagrams
- Lewis Dot Diagram Worksheet
- Stereochemistry – The Structures of Molecular Compounds
- Linear
- Trigonal Planar
- Tetrahedral
- Steps to Predicting Molecular Shapes
- Electronegativity
- Atom Size
- Polarity
- Polar Molecules
- Ionic Bonds
- Metallic Bonding
- Ionic Crystals
- Crystal formation
- Network Solids
- Intermolecular Forces
- Dipole-Dipole Forces
- Hydrogen Bonding
- Hydrogen Bonding in Water
- Hydrogen Bonds in Ice
- Unique Properties Reading
- London Dispersion Forces
- Factors Affecting Magnitude
- Structures and Properties of Compounds
- Time of Hydrogen Bonding
- Melting and Boiling Points
- Molecular Forces
- Mechanical Properties of Solids
- Conductivity
Last added presentations
- Direct heat utilization of geothermal energy
- Mechanics Lecture
- Newton’s Laws of Motion
- Mechanical, Electromagnetic, Electrical, Chemical and Thermal
- Ch 9 Nuclear Radiation
- Thermal Energy
- Magnetic field uses sound waves to ignite sun's ring of fire