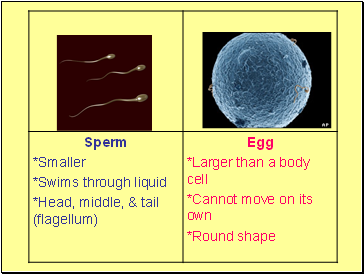
Sexual Reproduction in AnimalsPage
1
1
Slide 1
Sexual Reproduction in Animals
Slide 2
Slide 3
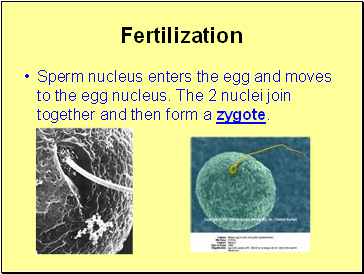
Fertilization
Sperm nucleus enters the egg and moves to the egg nucleus. The 2 nuclei join together and then form a zygote.
Slide 4
External Fertilization outside the body
Animals that breed in the water
Many hazards in the environment
Sperm and egg may not meet
Eggs or offspring may be eaten
May die due to environmental conditions
Temperature
Oxygen level
Slide 5
Large number of sperm and egg are released to overcome hazards
Hormones control behavior to have sperm and egg released at the same time.
Slide 6
Internal Fertilization within the female body
Land animals
Some aquatic animals
Shark
Octopus
Slide 7
Requires specialized sex organ to carry sperm to body of female
Watery environment needed for sperm to swim to the egg
Slide 8
After fertilization, zygote is enclosed in a protective shell and released OR remains and develops in female body
Zygote
Turtle laying eggs
Slide 9
Internal Fertilization
Fewer eggs needed
Well protected
Increased chance of fertilization
Parthenogenesis – development of unfertilized egg into an adult.- Bees & Wasps
Contents
- Sexual Reproduction in Animals
- Fertilization
- External Fertilization outside the body
- Internal Fertilization within the female body
Last added presentations
- Mechanical, Electromagnetic, Electrical, Chemical and Thermal
- Static and Kinetic Friction
- Radiation Safety and Operations
- Space Radiation
- Newton’s law of universal gravitation
- Solar Thermal Energy
- History of Modern Astronomy