Biochemistry. The Chemistry of LifePage
1
1
Slide 1
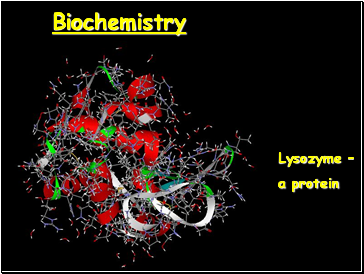
Biochemistry
Lysozyme –
a protein
Slide 2
Chemical Bonds
Covalent bonds form between atoms of nonmetals by sharing of electrons
- Molecules bond covalenty
Ionic bonds form between oppositely charged ions after the transfer of electrons
- Salts bond ionically
Slide 3
Organic Molecules
Organic molecules are molecules composed of carbon and hydrogen, and often containing other elements such as phosphorus, sulfur, oxygen and nitrogen
Slide 4
Elements of Life
Carbon
Hydrogen
Phosphorus
Sulfur
Oxygen
Nitrogen
Six elements make up 96% of your mass!
Slide 5
Carbohydrates
There are two types of carbohydrates:
The simple sugars
Glucose, sucrose, fructose (and many others)
The complex carbohydrates.
Carbohydrates that are made of long chains of sugars
Starches, cellulose, glycogen
Slide 6
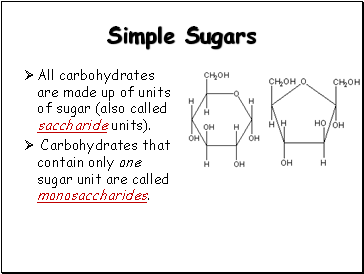
Simple Sugars
All carbohydrates are made up of units of sugar (also called saccharide units).
Carbohydrates that contain only one sugar unit are called monosaccharides.
Glucose
Fructose
Slide 7
Simple Sugars
Disaccharides have two sugar units bonded together.
For example, common table sugar is sucrose (below), a disaccharide that consists of a glucose unit bonded to a fructose unit.
Slide 8
Complex Carbohydrates
Complex carbohydrates are polymers of the simple sugars.
In other words, the complex carbohydrates are long chains of simple sugar units bonded together.
For this reason the complex carbohydrates are often referred to as polysaccharides.
Slide 9
Complex Carbohydrates
Starch (below) is a polymer of the monosaccharide glucose (n is the number of repeating glucose units and ranges in the 1,000's).
Starches and cellulose are complex carbohydrates used by plants for energy storage and structural integrity.
Slide 10
Complex Carbohydrates
Glycogen, another polymer of glucose, is a polysaccharide used by animals to store energy.
Both starch and glycogen are polymers of glucose.
1 2
Contents
- Chemical Bonds
- Organic Molecules
- Elements of Life
- Carbohydrates
- Simple Sugars
- Complex Carbohydrates
- Proteins
- Insulin
- Fats
Last added presentations
- Waves & Sound
- Solar Energy
- Soil and Plant Nutrition
- Thermal Energy
- Newton's laws of motion
- Friction
- Direct heat utilization of geothermal energy