MappingPage
1
1
Slide 1
Mapping
Slide 2
What is a map?
It is a representation of something (Earth, stars, solar system, a building, etc…
Slide 3
Uses of Maps
To determine where you are going.
To act as a model of Earth’s surface.
Used to locate various places
To show the distribution of various features or types of materials.
Slide 4
Quick Review of Latitude and Longitude
Latitude
Measured in degrees North and South of the Equator.
Lines drawn parallel to each other running west to east.
Slide 5
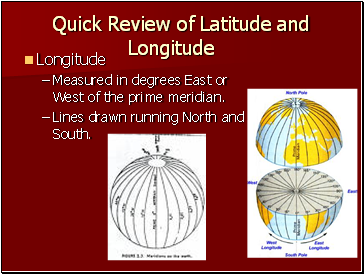
Quick Review of Latitude and Longitude
Longitude
Measured in degrees East or West of the prime meridian.
Lines drawn running North and South.
Slide 6
Topography
The lay of the land.
Shows relief using contour lines.
Relief- highs and lows of Earth’s surface.
Relief can be calculated
Take the difference between the highest point and the lowest.
Ex: Mountain peak 20 m. lake 10m
20m- 10m= 10m
The relief of this area is 10m
Slide 7
Reading a topographic map- Contour Lines
Lines on topographic maps.
Connect points of equal elevation.
Everything connected to that line has the same elevation.
Elevation- the distance something is above sea level. Sea level= 0m or 0ft.
Slide 8
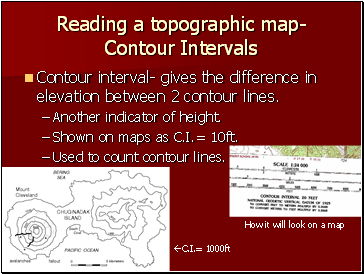
Reading a topographic map- Contour Intervals
Contour interval- gives the difference in elevation between 2 contour lines.
Another indicator of height.
Shown on maps as C.I.= 10ft.
Used to count contour lines.
C.I.= 1000ft
How it will look on a map
Slide 9
Reading a topographic map- Index Contours
A index contour is a contour line that is accentuated in thickness and is labeled with the appropriate measure of elevation.
Index contours occur every fifth contour line.
Help the map user read elevations on a map.
Red arrows indicate location of index contours.
Slide 10
Reading a topographic map- Streams
The direction a streams is flowing is shown on a topographic map by the way a contour line crosses the stream.
Contents
- What is a map?
- Uses of Maps
- Quick Review of Latitude and Longitude
- Topography
- Reading a topographic map- Contour Lines
- Reading a topographic map- Contour Intervals
- Reading a topographic map- Index Contours
- Reading a topographic map- Streams
- Reading a topographic map- Depression Contours
- Reading a topographic map- Hills
- Reading a topographic map- Slope
- Reading a topographic map- Benchmarks
- Reading a topographic map- Colors
- Reading a topographic map- Map Scale
- Reading a topographic map- Profiles
Last added presentations
- Buoyancy
- Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation
- Simulation at NASA for the Space Radiation Effort
- Geophysical Concepts, Applications and Limitations
- Newton’s law of universal gravitation
- Newton's laws of motion
- Motion