Atomic TheoryPage
1
1
Slide 1
Slide 2
Key words
Symbol
Mixture
Physical change
chemical change
Proton
Liquid
Thermal energy
Freezing
Compound
chemical reaction
Molecule
electron
Neutron
Gas
vaporization
coalesce
matter
atomic number
atomic mass
periodic table
nucleus
evaporation
boiling
element
conservation of mass
Period
ductile
magnetic
condensation
sublimation
atom
precipitate
malleable
conductor
corrosion
superheated gases coalesce
deposition=frost
heterogeneous mixture
homogeneous mixture
combustibility
Slide 3
Forces & Particles
Gravity Matter
Magnetism Anti-Matter
Strong Nuclear Forces
Weak Nuclear Forces
EVERYTHING in the Universe can be divided up into . . .
Slide 4
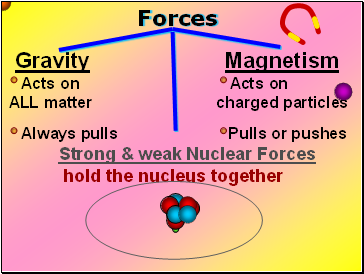
Forces
Gravity Magnetism
Acts on Acts on
ALL matter charged particles
Always pulls Pulls or pushes
Strong & weak Nuclear Forces
hold the nucleus together
Slide 5
Forces
Gravity Magnetism
Acts on Acts on
ALL matter charged particles
Always pulls Pulls or pushes
Magnetism is about 1040 times more powerful than gravity.
10,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000.
Slide 6
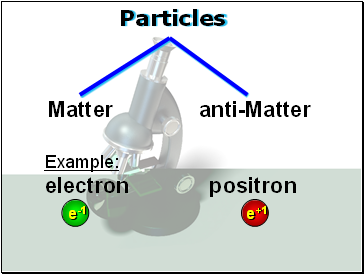
Particles
Matter anti-Matter
e+1
e-1
Example:
electron positron
Slide 7
The picture below shows three objects that can be classified in the same group. Which of the following statements is true for all three of these objects?
They are metals.
They rust rapidly.
They weigh the same.
They are the same color.
Slide 8
Which pair of elements is MOST similar?
Ca and F Na and Cl Ne and Ar Li and H
Slide 9
Copper is an element that is used in electrical wires. What is the smallest unit of copper that still maintains the characteristics of copper?
the atom
the electron
the nucleus
the proton
Slide 10
In making a pizza, which process involves a chemical change?
Mixing spices for the sauce
Contents
- Ionic bond
- Ion
- Cations
- Non-Metals
- Metalloids
- States of Matter
- Neon
- Valence Electrons
- Isotopes
- Electron Shells
- Atomic Number
- Hydrogen
- Helium
- Lithium
- Beryllium
- Boron
- Carbon
- Nitrogen
- Oxygen
- Fluorine
- Element
- Which of the following is a compound?
- Which symbol represents carbon?
- Particle accelerator
- Proton
- Neutron
- Electromagnetic radiation
- Which formulas represent compounds?
- Which is an example of a chemical change?
- Which statement is correct concerning the mass of a ball of clay?
- Mary wants to find the density of a small stone. Which tools will she need?
- Forces
- Particles
- Which pair of elements is MOST similar?
- Anions
- Solution
- Covalent bond
- Common chemicals
- Combustibility
- Reaction Types
- Precipitate
- Balancing equations
- Distilled water