Acid-Base Properties of SaltsPage
1
1
Slide 1
Acid-Base Properties of Salts
Slide 2
Acid-Base Properties of Salts
These salts simply dissociate in water:
KCl(s) K+(aq) + Cl-(aq)
Slide 3
Acid-Base Properties of Salts
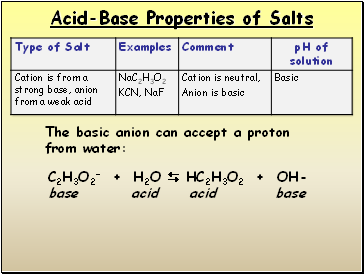
C2H3O2- + H2O HC2H3O2 + OH- base acid acid base
The basic anion can accept a proton from water:
Slide 4
Acid-Base Properties of Salts
NH4+(aq) NH3(aq) + H+(aq)
Acid Conjugate Proton
base
The acidic cation can act as a proton donor:
Slide 5
Acid-Base Properties of Salts
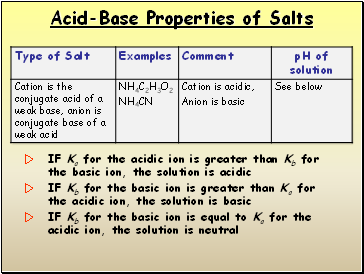
IF Ka for the acidic ion is greater than Kb for the basic ion, the solution is acidic
IF Kb for the basic ion is greater than Ka for the acidic ion, the solution is basic
IF Kb for the basic ion is equal to Ka for the acidic ion, the solution is neutral
Slide 6
Acid-Base Properties of Salts
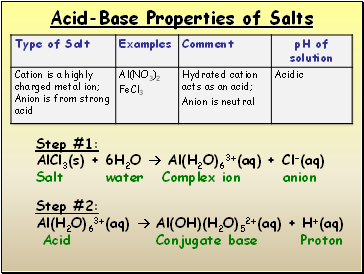
Step #1:
AlCl3(s) + 6H2O Al(H2O)63+(aq) + Cl-(aq)
Salt water Complex ion anion
Step #2:
Al(H2O)63+(aq) Al(OH)(H2O)52+(aq) + H+(aq)
Acid Conjugate base Proton
Slide 7
Effect of Structure on Acid-Base Properties
Increasing Acidity
Hypochlorous
acid
Chlorous
acid
Chloric
acid
Perchloric
acid
Contents
Last added presentations
- Newton’s Law of Gravity
- Radiation Safety and Operations
- Waves & Sound
- Mechanics Lecture
- Newton's Laws
- Practical Applications of Solar Energy
- Solar Energy