Solubility EquilibriaPage
1
1
Slide 1
Solubility Equilibria
Lead (II) iodide precipitates when potassium iodide is mixed with lead (II) nitrate.
Graphic: Wikimedia Commons user PRHaney
Slide 2
Ksp Values for Some Salts at 25C
Slide 3
Solving Solubility Problems
For the salt AgI at 25C, Ksp = 1.5 x 10-16
AgI(s) Ag+(aq) + I-(aq)
O
O
+x
+x
x
x
1.5 x 10-16 = x2
x = solubility of AgI in mol/L = 1.2 x 10-8 M
Slide 4
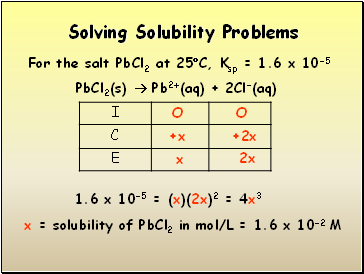
Solving Solubility Problems
For the salt PbCl2 at 25C, Ksp = 1.6 x 10-5
PbCl2(s) Pb2+(aq) + 2Cl-(aq)
O
O
+x
+2x
x
2x
1.6 x 10-5 = (x)(2x)2 = 4x3
x = solubility of PbCl2 in mol/L = 1.6 x 10-2 M
Slide 5
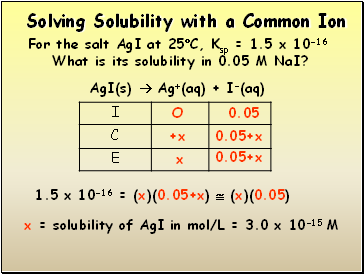
Solving Solubility with a Common Ion
For the salt AgI at 25C, Ksp = 1.5 x 10-16
What is its solubility in 0.05 M NaI?
AgI(s) Ag+(aq) + I-(aq)
0.05
O
+x
0.05+x
x
0.05+x
1.5 x 10-16 = (x)(0.05+x) (x)(0.05)
x = solubility of AgI in mol/L = 3.0 x 10-15 M
Slide 6
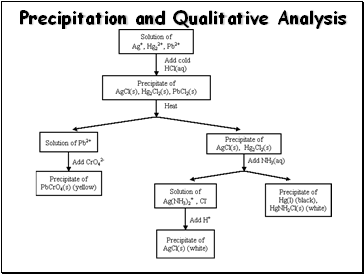
Precipitation and Qualitative Analysis
Slide 7
Complex Ions
A Complex ion is a charged species composed of:
1. A metallic cation
2. Ligands – Lewis bases that have a lone electron pair that can form a covalent bond with an empty orbital belonging to the metallic cation
Slide 8
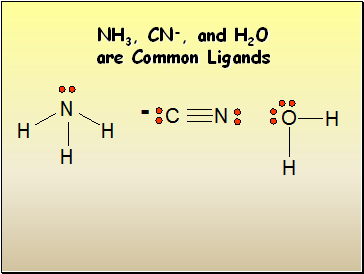
NH3, CN-, and H2O are Common Ligands
Slide 9
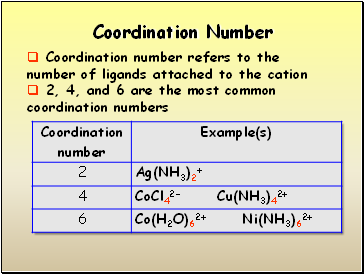
Coordination Number
Coordination number refers to the number of ligands attached to the cation
2, 4, and 6 are the most common coordination numbers
Slide 10
Complex Ions and Solubility
AgCl(s) Ag+ + Cl- Ksp = 1.6 x 10-10
Ag+ + NH3 Ag(NH3)+ K1 = 2.1 x 103
Ag(NH3)+ NH3 Ag(NH3)2+ K2 = 8.2 x 103
AgCl + 2NH3 Ag(NH3)2+ + Cl-
K = KspK1K2
Contents
- Solubility Equilibria
- Solving Solubility Problems
- Solving Solubility with a Common Ion
- Precipitation and Qualitative Analysis
- Complex Ions
- Coordination Number
- Complex Ions and Solubility
Last added presentations
- Motion
- Simulation at NASA for the Space Radiation Effort
- Heat-Energy on the Move
- Resource Acquisition and Transport in Vascular Plants
- Sound
- Mechanics Lecture
- Radiation