ResonancePage
1
1
Slide 1
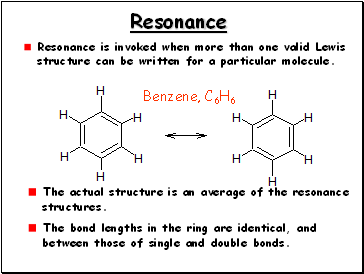
Resonance
Resonance is invoked when more than one valid Lewis structure can be written for a particular molecule.
The actual structure is an average of the resonance
structures.
Benzene, C6H6
The bond lengths in the ring are identical, and
between those of single and double bonds.
Slide 2
Resonance Bond Length and Bond Energy
Resonance bonds are shorter and stronger than single bonds.
Resonance bonds are longer and weaker than double
bonds.
Slide 3
Resonance in Ozone, O3
Neither structure is correct.
Oxygen bond lengths are identical, and intermediate to single and double bonds
Slide 4
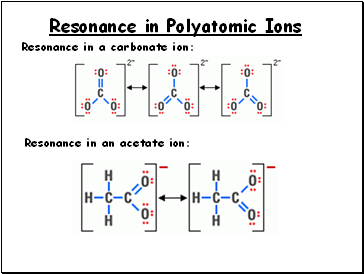
Resonance in Polyatomic Ions
Resonance in a carbonate ion:
Resonance in an acetate ion:
Slide 5
The Localized Electron Model
Lewis structures are an application of the “Localized Electron Model”
L.E.M. says: Electron pairs can be thought of as “belonging” to pairs of atoms when bonding
Resonance points out a weakness in the Localized Electron Model.
Slide 6
Models
Models are attempts to explain how nature operates on the microscopic level based on experiences in the macroscopic world.
Models can be physical as with this DNA model
Models can be mathematical
Models can be theoretical or philosophical
Slide 7
Fundamental Properties of Models
A model does not equal reality.
Models are oversimplifications, and are therefore often wrong.
Models become more complicated as they age.
We must understand the underlying assumptions in a model so that we don’t misuse it.
Contents
- Resonance
- Resonance Bond Length and Bond Energy
- Resonance in Ozone, O3
- Resonance in Polyatomic Ions
- The Localized Electron Model
- Models
- Fundamental Properties of Models
Last added presentations
- Madame Marie Curie
- Practical Applications of Solar Energy
- Solar Thermal Energy
- Newton’s third law of motion
- Health Physics
- Sound
- Newton’s law of universal gravitation