Phase ChangesPage
1
1
Slide 1
Phase Changes
Slide 2
CA Standards
Students know energy is released when a material condenses or freezes and is absorbed when a material evaporates or melts.
Slide 3
Water phase changes
Temperature remains
during a phase change.
constant
Slide 4
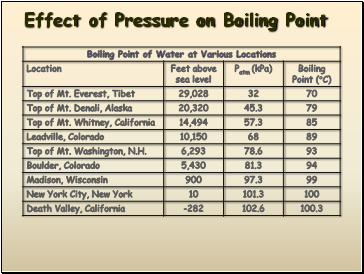
Effect of Pressure on Boiling Point
Slide 5
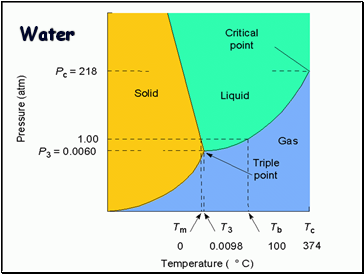
Phase Diagram
Represents phases as a function of temperature and pressure.
Critical temperature: temperature above which the vapor can not be liquefied.
Critical pressure: pressure required to liquefy AT the critical temperature.
Critical point: critical temperature and pressure (for water, Tc = 374°C and 218 atm).
Slide 6
Phase changes by Name
Slide 7
Water
Slide 8
Carbon dioxide
Phase Diagram for Carbon
dioxide
Slide 9
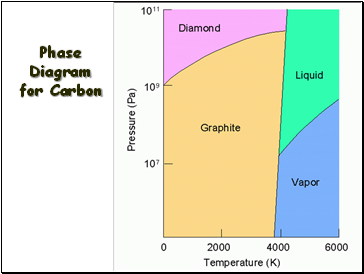
Carbon
Phase Diagram for Carbon
Slide 10
Phase Diagram for Sulfur
Contents
- Phase Changes
- Water phase changes
- Effect of Pressure on Boiling Point
- Phase Diagram
- Phase changes by Name
- Water
Last added presentations
- Motion
- Solar Energy
- Solar Thermal Energy
- Geophysical Concepts, Applications and Limitations
- The Effects of Radiation on Living Things
- Heat-Energy on the Move
- Newton’s law of universal gravitation
© 2010-2025 powerpoint presentations