The Cycles of the MoonPage
1
1
Slide 1
The Cycles of the Moon
The phases of the moon
The tides
Lunar eclipses
Solar eclipses
Slide 2
The Phases of the Moon
From Earth, we see different portions of the Moon’s surface lit by the sun, causing the phases of the Moon.
Slide 3
The Phases of the Moon
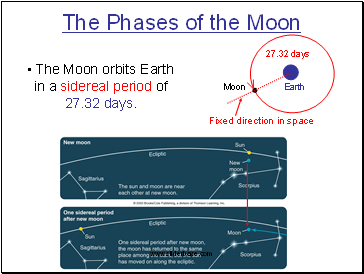
The Moon orbits Earth in a sidereal period of 27.32 days.
27.32 days
Earth
Moon
Fixed direction in space
Slide 4
Is the moon going to show the same lunar phase after one sidereal period?
Yes.
No, it will not have completed a full cycle of phases.
No, it will have completed more than a full cycle of phases.
Slide 5
The Phases of the Moon
The moon’s synodic period (to reach the same position relative to the sun) is 29.53 days (~ 1 month).
Fixed direction in space
Earth
Moon
Earth orbits around Sun => Direction toward Sun changes!
29.53 days
Slide 6
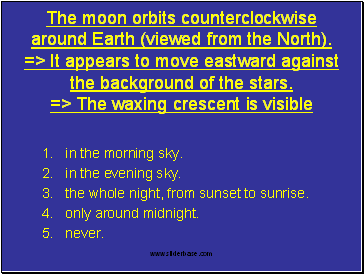
The moon orbits counterclockwise around Earth (viewed from the North). => It appears to move eastward against the background of the stars. => The waxing crescent is visible
in the morning sky.
in the evening sky.
the whole night, from sunset to sunrise.
only around midnight.
never.
Slide 7
The Phases of the Moon
New Moon → First Quarter → Full Moon
Evening Sky
Slide 8
The Phases of the Moon
Full Moon → Third Quarter → New Moon
Morning Sky
Waning
Slide 9
The Tides
The tides are caused by the difference of the Moon’s gravitational attraction on the water on Earth
Between the near side and the center of the Earth
Between the center and the far side of the Earth
→ 2 tidal maxima
→ 12-hour cycle
Slide 1
On the day of full moon, high tides occur …
around noon and 6 p.m.
around noon and midnight.
around 6 a.m. and 6 p.m.
around 6 p.m. and midnight.
Impossible to tell. The times of tides are not correlated with the phases of the moon.
Slide 11
Spring and Neap Tides
Contents
- The Cycles of the Moon
- The Phases of the Moon
- The Tides
- Spring and Neap Tides
- The Tidally Locked Orbit of the Moon
- A total lunar eclipse …
- Lunar Eclipses
- Solar Eclipses
Last added presentations
- Upcoming Classes
- Solar Energy
- Mechanics Lecture
- Newton’s Laws of Motion
- Gravitation
- Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation
- Soil and Plant Nutrition