Mirrors and LensesPage
1
1
Slide 1
Optics
Mirrors and Lenses
Slide 2
Reflection
We describe the path of light as straight-line rays
Reflection off a flat surface follows a simple rule:
angle in (incidence) equals angle out (reflection)
angles measured from surface “normal” (perpendicular)
incident ray
exit ray
reflected ray
Slide 3
Reflection Vocabulary
Real Image –
Image is made from “real” light rays that converge at a real focal point so the image is REAL
Can be projected onto a screen because light actually passes through the point where the image appears
Always inverted
Slide 4
Reflection Vocabulary
Virtual Image–
“Not Real” because it cannot be projected
Image only seems to be there!
Slide 5
Virtual Images in Plane Mirrors
Slide 6
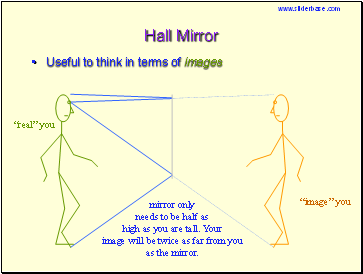
Hall Mirror
Useful to think in terms of images
mirror only
needs to be half as
high as you are tall. Your
image will be twice as far from you
as the mirror.
Slide 7
LEFT- RIGHT REVERSAL
AMBULANCE
Slide 8
Curved mirrors
What if the mirror isn’t flat?
light still follows the same rules, with local surface normal
Parabolic mirrors have exact focus
used in telescopes, backyard satellite dishes, etc.
also forms virtual image
Slide 9
Concave Mirrors
Curves inward
May be real or virtual image
View kacleaveland's map
Taken in a place with no name (See more photos or videos here)
"Have you ever approached a giant concave mirror? See your upside-down image suspended in mid-air. Walk through the image to see a new reflection, right-side-up and greatly magnified. In the background you see reflected a room full of visitors enjoying other
Slide 10
For a real object between f and the mirror, a virtual image is formed behind the mirror. The image is upright and larger than the object.
For a real object between f and the mirror, a virtual image is formed behind the mirror. The position of the image is found by tracing the reflected rays back behind the mirror to where they meet. The image is upright and larger than the object.
Contents
Last added presentations
- Solar Thermal Energy
- Buoyancy
- Newton’s Laws of Motion
- Solar Energy
- Direct heat utilization of geothermal energy
- Thermal Energy
- Newton’s law of universal gravitation