EcosystemsPage
1
1
Slide 1
Ecosystems
An ecosystem consists of all the organisms living in a community, as well as the abiotic factors with which they interact.
Ecosystems range from a microcosm, such as an aquarium, to a large area such as a lake or forest.
Regardless of an ecosystem’s size, its dynamics involve two main processes: energy flow and chemical cycling.
Energy flows through ecosystems while matter cycles within them.
Slide 2
Physical laws govern energy flow and chemical cycling in ecosystems
Laws of physics and chemistry apply to the transformations of energy and matter within the ecosystems, particularly energy flow.
The first law of thermodynamics states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed. Energy enters an ecosystem as solar radiation, is conserved, and is lost from organisms as heat.
The second law of thermodynamics states that every exchange of energy increases the entropy of the universe. In an ecosystem, energy conversions are not completely efficient, and some energy is always lost as heat.
Slide 3
Conservation of Mass
The law of conservation of mass states that matter cannot be created or destroyed.
Chemical elements are continually recycled within ecosystems.
In a forest ecosystem, most nutrients enter as dust or solutes in rain and are carried away in water.
Ecosystems are open systems, absorbing energy and mass and releasing heat and waste products.
Slide 4
Energy, Mass, and Trophic Levels
Autotrophs build organic molecules themselves using photosynthesis or chemosynthesis as an energy source.
Heterotrophs depend on the biosynthetic output of other organisms.
Energy and nutrients pass from primary producers (autotrophs) to primary consumers (herbivores) to secondary consumers (carnivores) to tertiary consumers (carnivores that feed on other carnivores).
Slide 5
Detritivores, or decomposers, are consumers that derive their energy from detritus, nonliving organic matter.
Prokaryotes and fungi are important detritivores.
Decomposition connects all trophic levels.
Slide 6
Fungi decomposing a dead tree
Slide 7
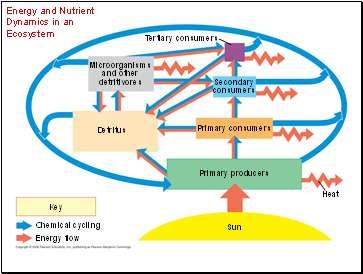
Energy and Nutrient Dynamics in an Ecosystem
Microorganisms
and other
detritivores
Tertiary consumers
Secondary
consumers
Primary consumers
Contents
- Ecosystems
- Physical laws govern energy flow and chemical cycling in ecosystems
- Conservation of Mass
- Energy, Mass, and Trophic Levels
- Energy and other limiting factors control primary production in ecosystems
- Primary Production in Aquatic Ecosystems
- Primary Production in Terrestrial Ecosystems
- Energy transfer between trophic levels is typically only 10% efficient
- Biological and geochemical processes cycle nutrients between organic and inorganic parts of an ecosystem
- Biogeochemical Cycles
- The Water Cycle
- The Carbon Cycle
- The Phosphorus Cycle
- Decomposition and Nutrient Cycling Rates
- Case Study: Nutrient Cycling in the Hubbard Brook Experimental Forest
- Acid Precipitation
- Toxins in the Environment
- Greenhouse Gases and Global Warming
- Depletion of Atmospheric Ozone
Last added presentations
- Madame Marie Curie
- Friction
- Sensory and Motor Mechanisms
- Radioactivity and Nuclear Reactions
- Thermal Energy
- Newton’s third law of motion
- Solar Energy