Animal DevelopmentPage
1
1
Slide 1
A Body-Building Plan
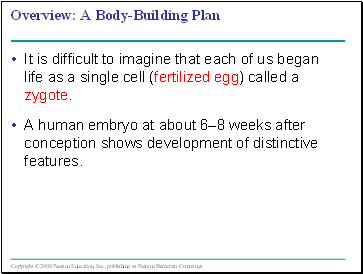
It is difficult to imagine that each of us began life as a single cell (fertilized egg) called a zygote.
A human embryo at about 6–8 weeks after conception shows development of distinctive features.
Slide 2
How did this complex embryo develop from a single fertilized egg?
1 mm
Slide 3
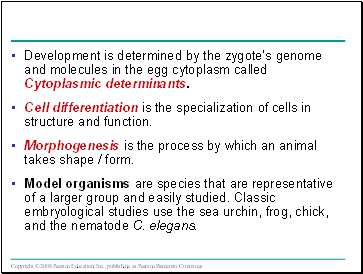
Development is determined by the zygote’s genome and molecules in the egg cytoplasm called Cytoplasmic determinants.
Cell differentiation is the specialization of cells in structure and function.
Morphogenesis is the process by which an animal takes shape / form.
Model organisms are species that are representative of a larger group and easily studied. Classic embryological studies use the sea urchin, frog, chick, and the nematode C. elegans.
Slide 4
After fertilization, embryonic development proceeds through cleavage, gastrulation, and organogenesis
Important events regulating development occur during fertilization and the three stages that build the animal’s body
Cleavage: cell division creates a hollow ball of cells called a blastula
Gastrulation: cells are rearranged into a three-layered gastrula
Organogenesis: the three germ layers interact and move to give rise to organs.
Slide 5
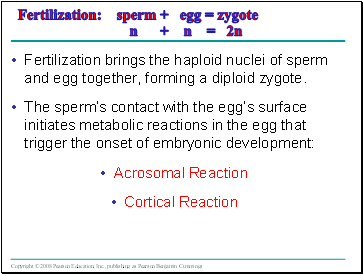
Fertilization: sperm + egg = zygote n + n = 2n
Fertilization brings the haploid nuclei of sperm and egg together, forming a diploid zygote.
The sperm’s contact with the egg’s surface initiates metabolic reactions in the egg that trigger the onset of embryonic development:
Acrosomal Reaction
Cortical Reaction
Slide 6
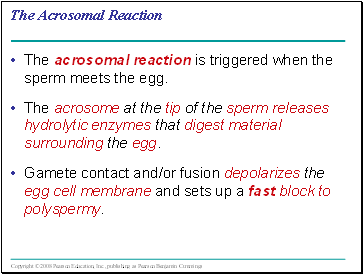
The Acrosomal Reaction
The acrosomal reaction is triggered when the sperm meets the egg.
The acrosome at the tip of the sperm releases hydrolytic enzymes that digest material surrounding the egg.
Gamete contact and/or fusion depolarizes the egg cell membrane and sets up a fast block to polyspermy.
Slide 7
The acrosomal and cortical reactions during sea urchin fertilization
Basal body (centriole)
Sperm head
Sperm-binding receptors
Acrosome
Jelly coat
Vitelline layer
Egg plasma membrane
Hydrolytic enzymes
Acrosomal process
Actin filament
Sperm nucleus
Sperm plasma membrane
Fused plasma membranes
Fertilization envelope
Cortical granule
Perivitelline space
Contents
- A Body-Building Plan
- The Cortical Reaction
- Activation of the Egg
- Fertilization in Mammals
- Cleavage = Rapid Mitosis / No Mass change
- Cleavage in an echinoderm embryo
- Gastrulation
- Gastrulation in the frog
- Gastrulation in the chick
- Organogenesis
- Developmental Adaptations of Amniotes
- Amniote ExtraEmbryonic Membranes
- Mammalian Development
- The Cytoskeleton, Cell Motility, and Convergent Extension
- Role of Cell Adhesion Molecules and the Extracellular Matrix
- The developmental fate of cells depends on their history and on inductive signals
- Two general principles underlie differentiation
- Formation of the Vertebrate Limb
- You should now be able to
Last added presentations
- Newton’s Law of Gravity
- Motion
- Newton’s Laws of Motion
- Soil and Plant Nutrition
- Gravitation
- Solar Thermal Energy
- Sound