Metals in industryPage
1
1
Slide 1
Metals in Industry, working with metals
Slide 2
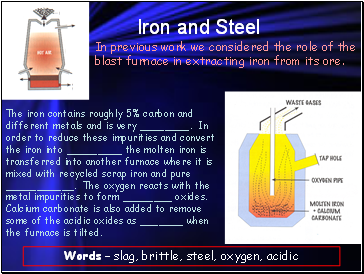
Iron and Steel
In previous work we considered the role of the blast furnace in extracting iron from its ore.
Slide 3
Making steel – the reactions
1) Mixing oxygen with silicon impurities:
2) Decomposition of limestone:
3) Adding these products together:
Slide 4
Titanium
Titanium is a strong metal used in planes, replacement hip joints, bikes etc. Two steps are used in its manufacture:
Step 1: Convert titanium dioxide (ore) to titanium chloride
Step 2: Displace the titanium using sodium or magnesium:
Slide 5
Aluminium
Aluminium is a fairly reactive metal that doesn’t corrode due to forming a thin layer of aluminium oxide. This explains why greenhouses don’t rust and don’t need to be painted.
A thicker layer of aluminium oxide can be made artificially. There are two stages:
1) Remove the natural layer by placing the aluminium in sodium hydroxide.
2) Use electrolysis on sulphuric acid with the aluminium as the positive electrode. This is called anodising.
Slide 6
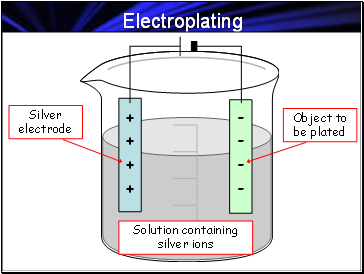
Electroplating
Solution containing silver ions
Contents
Last added presentations
- The Effects of Radiation on Living Things
- Mechanics Lecture
- Upcoming Classes
- Radiation
- Buoyancy
- Newton’s Laws of Motion
- Motion