Lab tests, results and sulphuric acidPage
1
1
Slide 1
Lab Tests, results, and Sulphuric acid
Slide 2
Testing for carbon dioxide
Slide 3
Adding acid to carbonates
Carbonates are compounds containing carbon and oxygen. When an acid is added to a carbonate the carbonate starts to fizz. A gas called _ _ is produced.
2
Slide 4
Flame tests
Slide 5
Flame tests
Compounds containing lithium, sodium, potassium, calcium and barium can be recognised by burning the compound and observing the colours produced:
Lithium
Red
Sodium
Yellow
Potassium
Lilac
Calcium
Brick red
Barium
Green
Slide 6
Metal ions
Metal compounds in a solution contain metal ions. For example, consider calcium chloride:
Calcium chloride has the formula CaCl2
Slide 7
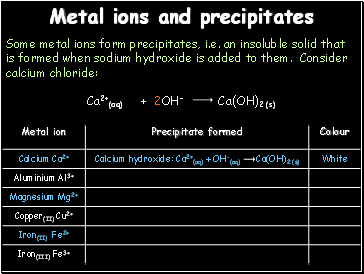
Metal ions and precipitates
Some metal ions form precipitates, i.e. an insoluble solid that is formed when sodium hydroxide is added to them. Consider calcium chloride:
2
Slide 8
Metal ions and precipitates
Some metal ions form precipitates, i.e. an insoluble solid that is formed when sodium hydroxide is added to them. Consider calcium chloride:
2
Slide 9
Testing for chloride and sulphate ions
Test 1: Chloride ions
Add a few drops of dilute nitric acid to the chloride ion solution followed by a few drops of silver nitrate.
Test 2: Sulphate ions
Add a few drops of dilute hydrochloric acid to the sulphate ion solution followed by a few drops of barium chloride.
Precipitate formed = silver chloride (white)
Precipitate formed = barium sulphate (white again)
For each test state: 1) The colour of the precipitate
2) What compound it is
Slide 10
Ammonium, nitrate, bromide and iodide ions
Ammonium ions:
Add sodium hydroxide and test the gas using damp litmus paper – ammonia gas turns damp litmus paper blue.
Nitrate ions:
Add sodium hydroxide followed by aluminium powder and test using damp litmus paper.
Bromide and iodide ions:
Add a few drops of dilute nitric acid followed by a few drops of silver nitrate solution. A pale yellow precipitate should be formed for bromide ions and a darker yellow precipitate for iodide ions.
1 2
Contents
- Testing for carbon dioxide
- Adding acid to carbonates
- Flame tests
- Metal ions
- Metal ions and precipitates
- Testing for chloride and sulphate ions
- Ammonium, nitrate, bromide and iodide ions
- Thermal decomposition
- Sulphuric acid
Last added presentations
- Newton’s Laws of Motion
- Heat-Energy on the Move
- Waves & Sound
- Sound
- Upcoming Classes
- Magnetic field uses sound waves to ignite sun's ring of fire
- Newton's Laws