What Makes Up Our GalaxyPage
1
1
Slide 1
The Size and Structure of the Milky Way Galaxy
We live in a new class of astronomical object
Slide 2
First… an advertisement for 29:52 “Exploration of the Solar System”
The other half of astronomy
Slide 3
Observations indicate the shape and size of the Milky Way Galaxy
Slide 4
Structure of the Milky Way
Disk
Bulge
Galactic center
Galactic halo
Question: what simple observation
Is consistent with a part of this picture?
Slide 5
A view of the Milky Way with an artist’s touch
Slide 6
Next topic: the motion of the Sun in the Milky Way (leads to something extremely interesting)
How does the Sun move in the Milky Way?
Slide 7
Next topic: the motion of the Sun in the Milky Way (leads to something extremely interesting)
How does the Sun move in the Milky Way?
V=220 km/sec
The sun moves in response to the gravitational force of
All the rest of the mass in the galaxy
Slide 8
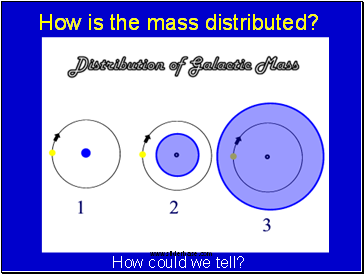
How is the mass distributed?
How could we tell?
Slide 9
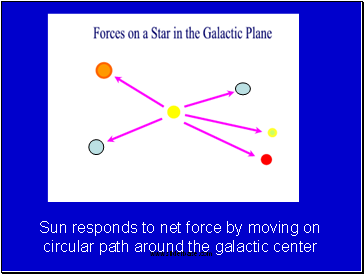
Force of Gravity acts on the Sun and all objects in the Galaxy
Gravity has magnitude and direction
Slide 10
Sun responds to net force by moving on circular path around the galactic center
Slide 11
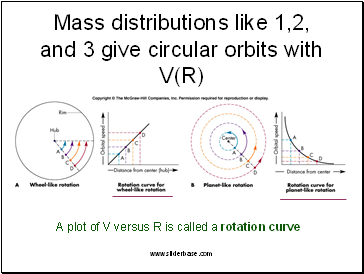
Mass distributions like 1,2, and 3 give circular orbits with V(R)
A plot of V versus R is called a rotation curve
Slide 12
The Observed Case for the Milky Way
No sign of the “root-R falloff”
Slide 13
Significance of the Rotation Curve for the Milky Way
Rotation curve stays high outside the bulk of the stars
Mass indicated by the rotation curve exceeds that in stars
Most of the mass of the Milky Way is in an unknown form of “Dark Matter”
Slide 14
The New View of the Milky Way
1 2
Contents
- The other half of astronomy
- Observations indicate the shape and size of the Milky Way Galaxy
- Structure of the Milky Way
- A view of the Milky Way with an artist’s touch
- The New View of the Milky Way
- At the Very Center
Last added presentations
- Friction
- Newton's laws of motion
- Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation
- Resource Acquisition and Transport in Vascular Plants
- Newton’s Laws of Motion
- Radiation
- Heat-Energy on the Move