Understanding AstronomyPage
1
1
Slide 1
Light and Telescopes
Slide 2
What do you think?
What is the main purpose of a telescope?
Why do stars twinkle?
Slide 3
If you pass white light through a prism, it separates into its component colors.
R.O.Y. G. B.I.V
spectrum
Slide 4
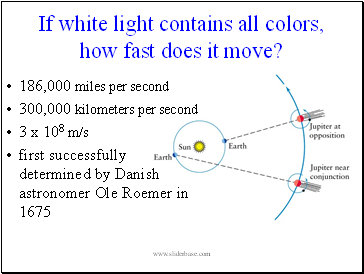
If white light contains all colors, how fast does it move?
186,000 miles per second
300,000 kilometers per second
3 x 108 m/s
first successfully determined by Danish astronomer Ole Roemer in 1675
Slide 5
But, what is light?
In the 17th Century, Isaac Newton argued that light was composed of little particles while Christian Huygens suggested that light travels in the form of waves.
In the 19th Century, Thomas Young demonstrated that light bends slightly around corners and acts like interfering waves.
Slide 6
Thomas Young’s interference experiment
Slide 7
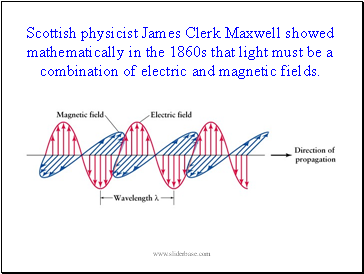
Scottish physicist James Clerk Maxwell showed mathematically in the 1860s that light must be a combination of electric and magnetic fields.
Slide 8
It wasn’t until 1905 that our current understanding of the nature of light emerged. Einstein showed that light sometimes behaves as particles and sometimes as waves.
Photon energy = Plank’s constant x speed of light / wavelength
Slide 9
Visible light is only one type of electromagnetic radiation emitted by stars
Each type of EM radiation travels at exactly the same speed - the speed of light!
Slide 10
Not all EM radiation can penetrate Earth’s atmosphere.
Slide 11
What is Light and Why Would Astronomers Want to Study the Properties of Light?
Sometimes we say light is made of waves
Sometime we say light is made of particles called photons
Moves very fast, at 186 000 miles per second
300,000 km per second
consider a prism .
Slide 12
If you pass white light through a prism, it separates into its component colors.
Contents
- What do you think?
- SOFIA - the Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy
- Consider Orion in Different Wavelengths of Light!
- High Energy Gamma Rays - Compton Gamma Ray Observatory (GRO) Satellite
- The Sky’s emission of Gamma Rays
- The Very Large Array (VLA) in New Mexico
- Dividing Light Into a Spectrum
- Spectra
- Three main functions of a telescope
- A Charge-Coupled Device (CCD)
Last added presentations
- Newton’s law of universal gravitation
- Sensory and Motor Mechanisms
- Buoyancy
- Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation
- Practical Applications of Solar Energy
- Magnetic field uses sound waves to ignite sun's ring of fire
- Solar Energy