How Elements BondPage
1
1
Slide 1
Ionic, Covalent, and Metallic bonding
Slide 2
Bond Formation
The positive sodium ion and the negative chloride ion are strongly attracted to each other.
2
This attraction, which holds the ions close together, is a type of chemical bond called an ionic bond.
Slide 3
Bond Formation
The compound sodium chloride, or table salt, is formed.
2
A compound is a pure substance containing two or more elements that are chemically bonded.
Slide 4
More Gains and Losses
Can elements lose or gain more than one electron?
2
The element magnesium, Mg, in Group 2 has two electrons in its outer energy level.
Magnesium can lose these two electrons and achieve a completed energy level.
Slide 5
More Gains and Losses
Some atoms, such as oxygen, need to gain two electrons to achieve stability.
How Elements Bond
2
The two electrons released by one magnesium atom could be gained by a single atom of oxygen.
When this happens, magnesium oxide (MgO) is formed.
Slide 6
Convalent Bonds—Sharing
Some atoms are unlikely to lose or gain electrons because the number of electrons in their outer levels makes this difficult.
How Elements Bond
2
The alternative is sharing electrons.
Slide 7
The Convalent Bond
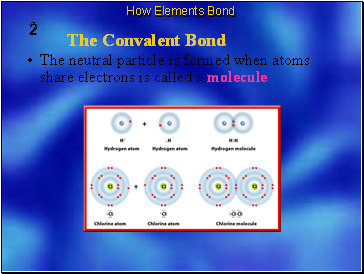
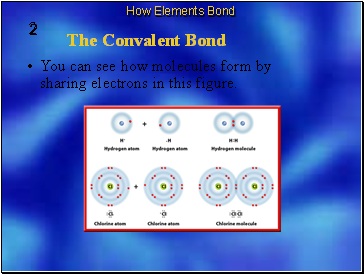
The chemical bond that forms between nonmetal atoms when they share electrons is called a covalent bond.
How Elements Bond
2
Click image to view movie.
Slide 8
The Convalent Bond
Shared electrons are attracted to the nuclei of both atoms.
How Elements Bond
2
They move back and forth between the outer energy levels of each atom in the covalent bond.
So, each atom has a stable outer energy level some of the time.
Slide 9
The Convalent Bond
The neutral particle is formed when atoms share electrons is called a molecule
How Elements Bond
2
Slide 10
The Convalent Bond
How Elements Bond
2
A molecule is the basic unit of a molecular compound.
Slide 11
1 2
Contents
Last added presentations
- Geophysical Concepts, Applications and Limitations
- The Effects of Radiation on Living Things
- Heat-Energy on the Move
- Mechanics Lecture
- Space Radiation
- Magnetic field uses sound waves to ignite sun's ring of fire
- Newton’s law of universal gravitation