Polar Covalent Bonds Acids and BasesPage
1
1
Slide 1
2. Polar Covalent Bonds: Acids and Bases
Based on McMurry’s Organic Chemistry, 7th edition
Slide 2
2
Why this chapter?
Description of basic ways chemists account for chemical reactivity.
Establish foundation for understanding specific reactions discussed in subsequent chapters.
Slide 3
3
Polar Covalent Bonds: Electronegativity
Covalent bonds can have ionic character
These are polar covalent bonds
Bonding electrons attracted more strongly by one atom than by the other
Electron distribution between atoms is not symmetrical
Slide 4
4
Bond Polarity and Electronegativity
Electronegativity (EN): intrinsic ability of an atom to attract the shared electrons in a covalent bond
Differences in EN produce bond polarity
Arbitrary scale. As shown in Figure 2.2, electronegativities are based on an arbitrary scale
F is most electronegative (EN = 4.0), Cs is least (EN = 0.7)
Metals on left side of periodic table attract electrons weakly, lower EN
Halogens and other reactive nonmetals on right side of periodic table attract electrons strongly, higher electronegativities
EN of C = 2.5
Slide 5
5
The Periodic Table and Electronegativity
Slide 6
6
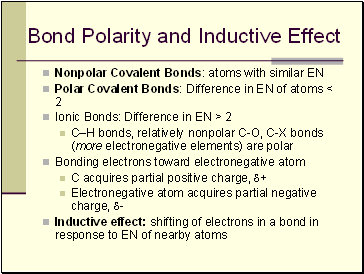
Bond Polarity and Inductive Effect
Nonpolar Covalent Bonds: atoms with similar EN
Polar Covalent Bonds: Difference in EN of atoms < 2
Ionic Bonds: Difference in EN > 2
C–H bonds, relatively nonpolar C-O, C-X bonds (more electronegative elements) are polar
Bonding electrons toward electronegative atom
C acquires partial positive charge, +
Electronegative atom acquires partial negative charge, -
Inductive effect: shifting of electrons in a bond in response to EN of nearby atoms
Slide 7
7
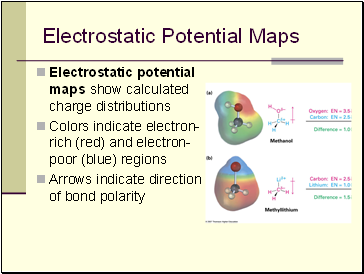
Electrostatic Potential Maps
Electrostatic potential maps show calculated charge distributions
Colors indicate electron-rich (red) and electron-poor (blue) regions
Arrows indicate direction of bond polarity
Slide 8
8
Polar Covalent Bonds: Dipole Moments
Molecules as a whole are often polar from vector summation of individual bond polarities and lone-pair contributions
Strongly polar substances soluble in polar solvents like water; nonpolar substances are insoluble in water.
Contents
- Why this chapter?
- Polar Covalent Bonds: Electronegativity
- Bond Polarity and Electronegativity
- Electrostatic Potential Maps
- Polar Covalent Bonds: Dipole Moments
- Formal Charges
- Resonance
- Rules for Resonance Forms
- Drawing Resonance Forms
- Pentanedione
- Acids and Bases: The Brønsted–Lowry Definition
- Acid and Base Strength
- Predicting Acid–Base Reactions from pKa Values
- Organic Acids and Organic Bases
- Acids and Bases: The Lewis Definition
- Molecular Models
- Noncovalent Interactions
Last added presentations
- Solar Thermal Energy
- Waves & Sound
- Upcoming Classes
- Mechanics Lecture
- Geophysical Concepts, Applications and Limitations
- Newton’s law of universal gravitation
- Motion