How many protons, electrons, and neutrons are in an atomPage
1
1
Slide 1
How many protons, electrons, and neutrons are in an atom?
Slide 2
Step 1
Use your periodic table to find an element
Slide 3
Step 2
The number of Protons (+ charge)
The atomic number = # protons
Kr has 36 protons
Slide 4
Step 3
The number of Electrons (- charge)
Remember atoms have no overall charge.
Atoms must have an equal # of protons and electrons
#protons=#electrons
Kr has 36 electrons
Slide 5
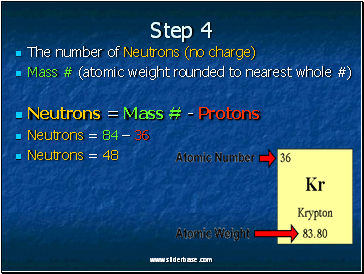
Step 4
The number of Neutrons (no charge)
Mass # (atomic weight rounded to nearest whole #)
Neutrons = Mass # - Protons
Neutrons = 84 – 36
Neutrons = 48
Slide 6
Summary
Number of Protons = Atomic #
Number of Electrons = Protons
Number of Neutrons = Mass # - Protons
Slide 7
Problems
Find the protons (p+), electrons (e-), neutrons (n) of Oxygen
Find the p+, e-, n of Xenon (Xe)
Find the p+, e-, n of Zirconium (Zr)
Slide 8
Oxygen (O) p+, e-, n
Number of Protons = Atomic #
Number of Electrons = Protons
Number of Neutrons = Mass # - Protons
Protons = 8
Electrons = 8
Neutrons = 16-8 = 8
Slide 9
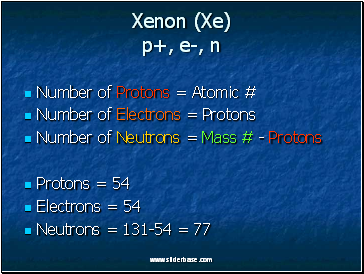
Xenon (Xe) p+, e-, n
Number of Protons = Atomic #
Number of Electrons = Protons
Number of Neutrons = Mass # - Protons
Protons = 54
Electrons = 54
Neutrons = 131-54 = 77
Slide 10
Zirconium (Zr) p+, e-, n
Number of Protons = Atomic #
Number of Electrons = Protons
Number of Neutrons = Mass # - Protons
Protons = 40
Electrons = 40
Neutrons = 91-40 = 51
Contents
Last added presentations
- Newton’s law of universal gravitation
- Sensory and Motor Mechanisms
- Soil and Plant Nutrition
- Simulation at NASA for the Space Radiation Effort
- Mechanical, Electromagnetic, Electrical, Chemical and Thermal
- Space Radiation
- The Effects of Radiation on Living Things