Chemical reactionsPage
1
1
Slide 1
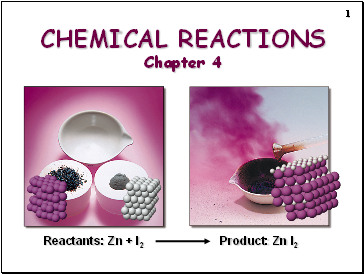
CHEMICAL REACTIONS Chapter 4
Reactants: Zn + I2
Product: Zn I2
Slide 2
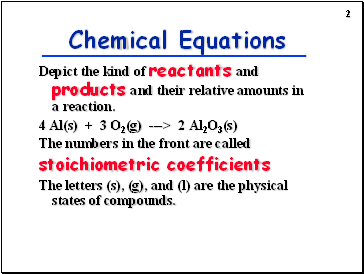
Chemical Equations
Depict the kind of reactants and products and their relative amounts in a reaction.
4 Al(s) + 3 O2(g) ---> 2 Al2O3(s)
The numbers in the front are called
stoichiometric coefficients
The letters (s), (g), and (l) are the physical states of compounds.
Slide 3
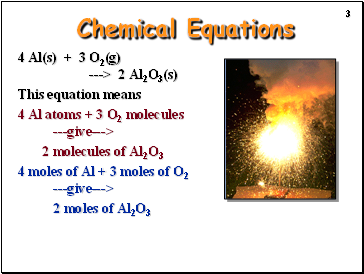
Chemical Equations
4 Al(s) + 3 O2(g) ---> 2 Al2O3(s)
This equation means
4 Al atoms + 3 O2 molecules ---give--->
2 molecules of Al2O3
4 moles of Al + 3 moles of O2 ---give--->
2 moles of Al2O3
Slide 4
Chemical Equations
Because the same atoms are present in a reaction at the beginning and at the end, the amount of matter in a system does not change.
The Law of the Conservation of Matter
Demo of conservation of matter, See Screen 4.3.
Slide 5
Because of the principle of the conservation of matter,
an equation must be balanced.
It must have the same number of atoms of the same kind on both sides.
Chemical Equations
Slide 6
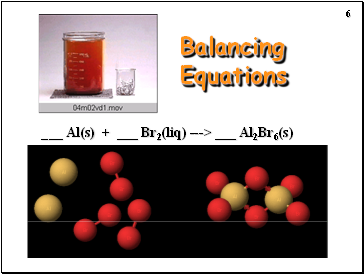
Balancing Equations
_ Al(s) + _ Br2(liq) ---> _ Al2Br6(s)
Slide 7
Balancing Equations
C3H8(g) + _ O2(g) ----> _CO2(g) + _ H2O(g)
B4H10(g) + _ O2(g) ----> _ B2O3(g) + _ H2O(g)
Slide 8
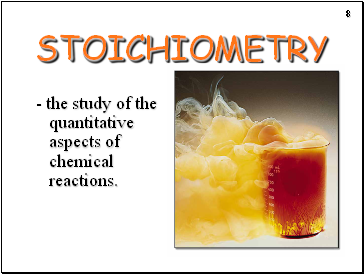
Stoichiometry
- the study of the quantitative aspects of chemical reactions.
Slide 9
STOICHIOMETRY
It rests on the principle of the conservation of matter.
2 Al(s) + 3 Br2(liq) ------> Al2Br6(s)
Slide 10
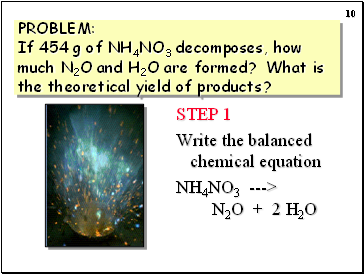
PROBLEM: If 454 g of NH4NO3 decomposes, how much N2O and H2O are formed? What is the theoretical yield of products?
STEP 1
Write the balanced chemical equation
NH4NO3 ---> N2O + 2 H2O
Slide 11
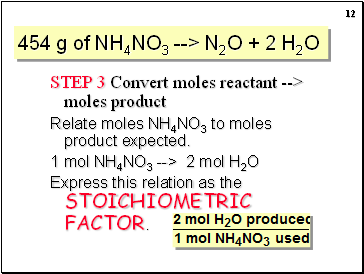
454 g of NH4NO3 --> N2O + 2 H2O
STEP 2 Convert mass reactant (454 g) --> moles
STEP 3 Convert moles reactant (5.68 mol) --> moles product
Slide 12
Contents
- Chemical Equations
- Balancing Equations
- Stoichiometry
- General plan for stoichiometry calculations
- Reactions Involving a Limiting reactant
- Limiting reactants
- Reaction to be Studied
- Using Stoichiometry to Determine a Formula
Last added presentations
- Thermal Energy
- Solar Thermal Energy
- Newton’s Law of Gravity
- Simulation at NASA for the Space Radiation Effort
- Geophysical Concepts, Applications and Limitations
- Heat-Energy on the Move
- Waves & Sound