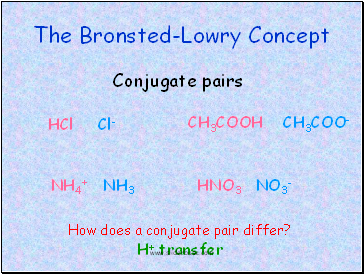Acids and Bases. General propertiesPage
1
1
Slide 1
Acids and Bases
PGCC CHM 101 Sinex
Slide 2
General properties
ACIDS
Taste sour
Turn litmus
React with active metals – Fe, Zn
React with bases
BASES
Taste bitter
Turn litmus
Feel soapy or slippery (react with fats to make soap)
React with acids
blue to red
red to blue
Slide 3
Definitions
Acids – produce H+
Bases - produce OH-
Acids – donate H+
Bases – accept H+
Acids – accept e- pair
Bases – donate e- pair
Arrehenius
Bronsted-Lowry
Lewis
only in water
any solvent
used in organic chemistry,
wider range of substances
Slide 4
Examples
Arrhenius
Bronsted-Lowry
Lewis
HCl
NaOH
HCl
NH3
:NH3
BF3
HCN
The hydrogen ion in aqueous solution
H+ + H2O H3O+ (hydronium ion)
Slide 5
The Bronsted-Lowry Concept
Conjugate pairs
HCl Cl-
CH3COOH CH3COO-
NH4+ NH3
HNO3 NO3-
How does a conjugate pair differ?
H+ transfer
Slide 6
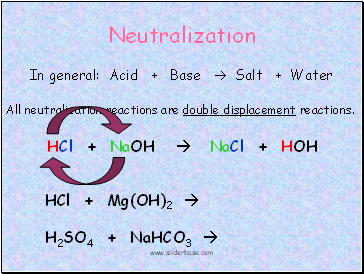
Neutralization
In general: Acid + Base Salt + Water
All neutralization reactions are double displacement reactions.
HCl + NaOH NaCl + HOH
HCl + Mg(OH)2
H2SO4 + NaHCO3
Slide 7
H2O H+ + OH-
Does pure water conduct electrical current?
(H+)(OH-) = 10-14
For pure water: (H+) = (OH-) = 10-7M
This is neutrality and at 25oC is a pH = 7.
Water is a very, very, very weak electrolyte.
How are (H+) and (OH-) related?
water
Slide 8
HA
Let’s examine the behavior of an acid, HA, in aqueous solution.
What happens to the HA molecules in solution?
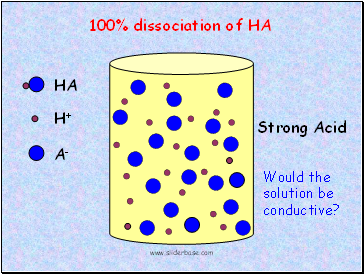
Slide 9
HA
H+
A-
Strong Acid
100% dissociation of HA
Would the solution be conductive?
Slide 10
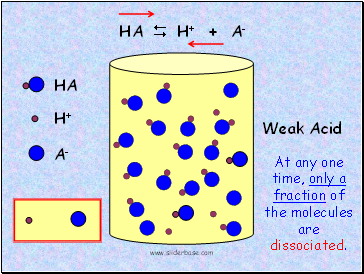
HA
H+
A-
Weak Acid
Partial dissociation of HA
Would the solution be conductive?
Slide 11
HA
H+
A-
Weak Acid
Contents
- General properties
- Definitions
- The Bronsted-Lowry Concept
- Neutralization
- Strong and Weak Acids/Bases
- What is acid rain?
- Dilution
- Titration Calculation
Last added presentations
- Newton’s law of universal gravitation
- Thermal Energy
- The Effects of Radiation on Living Things
- Radiation Safety and Operations
- Heat-Energy on the Move
- Motion
- Newton's Laws