Genetic problemsPage
1
1
Slide 1
Genetic problems
Slide 2
Question #1
How many different kinds of gametes could the following individuals produce?
1. aaBb
2. CCDdee
3. AABbCcDD
4. MmNnOoPpQq
5. UUVVWWXXYYZz
Slide 3
Question #1
Remember the formula 2n
Where n = # of heterozygous
1. aaBb = 2
2. CCDdee = 2
3. AABbCcDD = 4
4. MmNnOoPpQq = 32
5. UUVVWWXXYYZz = 2
Slide 4
Question #2
In dogs, wire-haired is due to a dominant gene (W), smooth-haired is due to its recessive allele (w).
WW, Ww = wire haired
ww = smooth haired
Slide 5
Question #2A
If a homozygous wire-haired dog is mated with a smooth-haired dog, what type of offspring could be produced.
W W
w
w
Slide 6
Question #2A
W W
w Ww Ww
fg F1 generation
w Ww Ww all heterozygous
Slide 7
Question #2B
What type(s) of offspring could be produced in the F2 generation?
Must breed the F1 generation to get the F2.
Results of F1 Cross: Ww x Ww
Slide 8
Question #2B
W w
W WW Ww F2 generation
w Ww ww
genotype: 1:2:1 ratio
phenotype: 3:1 ratio
Slide 9
Question #2C
Two wire-haired dogs are mated. Among the offspring of their first litter is a smooth-haired pup.
If these, two wire-haired dogs mate again, what are the chances that they will produce another smooth-haired pup?
What are the chances that the pup will wire-haired pup?
Slide 10
Question #2C
W w
W WW Ww F2 generation
w Ww ww
- 1/4 or 25% chance for smooth-haired
- 3/4 or 75% chance for wire-haired
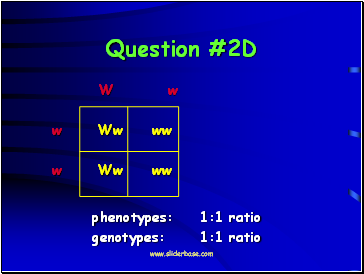
Slide 11
Question #2D
A wire-haired male is mated with a smooth-haired female. The mother of the wire-haired male was smooth-haired.
What are the phenotypes and genotypes of the pups they could produce?
Show the results of crossing: Ww x ww
Slide 12
Contents
Last added presentations
- Solar Thermal Energy
- Mechanical, Electromagnetic, Electrical, Chemical and Thermal
- Newton’s Laws of Motion
- Magnetic field uses sound waves to ignite sun's ring of fire
- Geophysical Concepts, Applications and Limitations
- Solar Energy
- Radiation Safety and Operations