Plant DiversityPage
1
1
Slide 1
Plant Diversity
Adapted from Prentice Hall
Slide 2
What are Plants?
Plants are multicellular eukaryotes that have cell walls made of cellulose.
Plants develop from multicellular embryos and carry out photosynthesis using the green pigments chlorophyll a and b
Slide 3
Plant Life Cycle
Plants go through Alternation of Generations
Slide 4
The Plant Life Cycle
During the two phases of the life cycle, mitosis and meiosis alternate to produce the two types of reproductive cells — gametes and spores.
The diploid (2N) phase is called the sporophyte, or spore-producing plant.
The haploid (N) phase is called the gametophyte, or gamete-producing plant.
Slide 5
What Plants Need to Survive
In order to survive, plants need:
sunlight
water and minerals
gas exchange (need CO2 & give off O2)
transport of water and nutrients throughout the plant body
Slide 6
Early Plants
The first plants evolved from an organism similar to the multicellular green algae living today.
Slide 7
Early Plants
The oldest known plant fossils, about 450 million years old, are similar to today’s mosses.
They had a simple structure and grew close to the ground.
Slide 8
Overview of the Plant Kingdom
Plants are divided into four groups based on these features:
water-conducting tissues
seeds
flowers
Plants are also classified by other features, including reproductive structures and body plan.
Slide 9
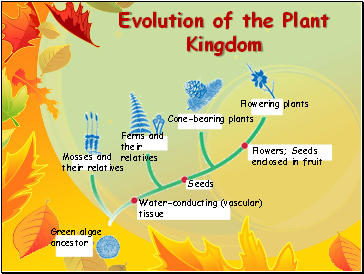
Evolution of the Plant Kingdom
Flowering plants
Cone-bearing plants
Ferns and their relatives
Mosses and their relatives
Flowers; Seeds enclosed in fruit
Water-conducting (vascular) tissue
Seeds
Green algae ancestor
Slide 10
Bryophytes
Moss & Fern
Slide 11
Groups of Bryophytes
Mosses and their relatives are called bryophytes, or nonvascular plants.
They do not have vascular tissues, or specialized tissues that conduct water and nutrients.
Contents
- Perennials
- Flowers and Fruits
- Flower Anatomy
- Diversity of Angiosperms
- Annuals, Biennials, and Perennials
- Diversity of Angiosperms
- What are Plants?
- The Plant Life Cycle
- What Plants Need to Survive
- Early Plants
- Overview of the Plant Kingdom
- Groups of Bryophytes
- Structure of a Moss Plant
- Human Use of Mosses
- Evolution of Vascular Tissue
- More Vascular Tissue
- Evolution of Vascular Tissue
- Ferns and Their Relatives
- Life Cycle of Ferns
- Fern Gametophyte
- Seed Plants
- Reproduction Free From Water
- Seeds
- Gymnosperms—Cone Bearers
- Conifers -The Cedars
Last added presentations
- Sound
- Radiation
- History of Modern Astronomy
- Radioactivity and Nuclear Reactions
- Newton’s Laws of Motion
- Magnetic field uses sound waves to ignite sun's ring of fire
- Newton’s laws of motion