Properties of WaterPage
1
1
Slide 1
The Chemistry of Life
Properties of Water
Slide 2
The Water Molecule
Neutral Charge Ė ZERO
Have no charge
Have an Equal number of p+ and e-
Charges arenít evenly distributed
Slide 3
The Water Molecule
Polarity
A water molecule is polar because there is an uneven distribution of electrons between the oxygen and hydrogen atoms.
(-)
(+)
Slide 4
Hydrogen Bonds
Polar water molecules act like magnets and attract each other
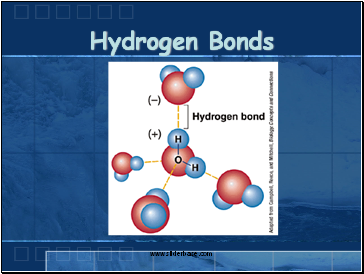
Hydrogen Bonds
The attraction of the Hydrogen end (+) of one molecule for the Oxygen end (-) of another water molecule.
They are strong bonds that form between molecules (CO2, H2O, Ö)
Slide 5
Hydrogen Bonds
Slide 6
Cohesion
The attraction between molecules of the same substance (e.g. water).
H2O attracting other H2O molecules
Allows some insects and spiders to walk on water.
Slide 7
Adhesion & Capillarity
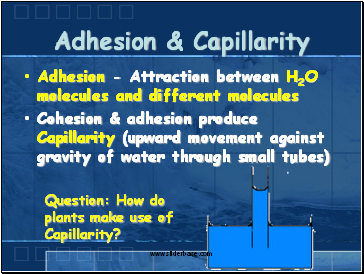
Adhesion - Attraction between H2O molecules and different molecules
Cohesion & adhesion produce Capillarity (upward movement against gravity of water through small tubes)
Question: How do plants make use of Capillarity?
Slide 8
Solutions & Suspensions
Water is usually part of a mixture.
Because so many things dissolve in water, it is called the Universal Solvent
There are two types of mixtures:
Solutions
Suspensions
Slide 9
Properties of Solutions
Ionic compounds disperse as ions in water (+ions & -ions spread out among polar water molecules)
Solutions are Evenly distributed mixtures
SOLUTE
Substance that is being dissolved
SOLVENT
Dissolving Substance for the solute
Slide 10
Ionic Solutions
Na+ ions will be attracted to WHAT END of the water molecule?
Slide 11
Suspensions
Substances that donít dissolve but separate into tiny pieces.
Water keeps the pieces suspended so they donít settle out.
1 2
Contents
- The Water Molecule
- Hydrogen Bonds
- Cohesion
- Adhesion & Capillarity
- Solutions & Suspensions
- Properties of Solutions
- Ionic Solutions
- Suspensions
- Acids, Bases & pH
- The pH Scale
- Acids
- Bases
- Buffers
Last added presentations
- Solar Energy
- Gravitation
- History of Modern Astronomy
- Radiation
- Solar Thermal Energy
- Radioactivity and Nuclear Reactions
- Newtonís laws of motion