Cause and effect of mutationPage
1
1
Slide 1
Cause and effect of mutation
L Mathias
Slide 2
What causes mutation
Spontaneous
Increases caused by environmental factors
UV light
X-rays
Benzene, formaldehyde, carbon tetrachloride
Slide 3
Gametic and somatic mutations
Gametic testis of males, ovaries of females, inherited
Somatic in normal body cells occuring beyond zygote formation, not inherited but may effect the person during their lifetime. Chimaeras
Slide 4
Mutagens and their effects
Ionising radiation Nuc radiation, xrays, gamma rays (e.g. medical treatment) associated with development of cancers (e.g. leukaemia, thyroid cancer and skin cancer
Slide 5
Mutagens and their effects
Viruses and microorganisms integrate into human chromosome, upset genes and can trigger cancer
Slide 6
Mutagens and their effects
Environmental poisons Organic solvents such as formaldehyde, tobacco, coal tars, benzene, asbestos, some dyes
Slide 7
Mutagens and their effects
Alcohol and diet High alcohol intake increase the risk of some cancers. Diet high in fat and those containing burned or highly preserved meat
Slide 8
The effect of muations
Not all are harmful
Survival advantage
Most common among bacteria and viruses but also seen in insects
If no selective pressure may remain in population
Slide 9
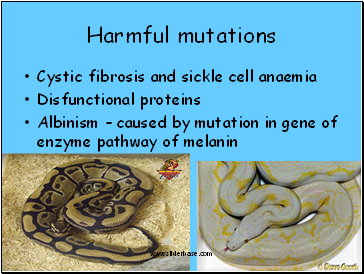
Harmful mutations
Cystic fibrosis and sickle cell anaemia
Disfunctional proteins
Albinism caused by mutation in gene of enzyme pathway of melanin
Slide 10
Beneficial mutations
Bacteria antibiotic resistance through mutation, transfer between bacterial species
Superbugs such as MRSA have arisen this way
RNA viruses such as HIV mutates its protein coat so that the host human is unable to make antibodies quick enough against it
Slide 11
Neutral mutations
Neither harmful or beneficial to the organism but may be important in an evolutionary sense
1 2
Contents
- Cause and effect of mutation
- Gametic and somatic mutations
- Mutagens and their effects
- The effect of muations
- Harmful mutations
- Beneficial mutations
- Neutral mutations
Last added presentations
- Static and Kinetic Friction
- Ch 9 Nuclear Radiation
- Madame Marie Curie
- Sensory and Motor Mechanisms
- Newtons third law of motion
- Simulation at NASA for the Space Radiation Effort
- History of Modern Astronomy