FungiPage
1
1
Slide 1
Slide 2
Slide 3
Slide 4
Fungal Characteristics
1)Cell wall made of Chitin
2)Heterotrophs and major Decomposers
3)Body is made of Long filaments of hyphae which form a mycelium
4)Reproduce sexually and asexually
Asexually by spores
Sexually by mating of hyphae filaments
Slide 5
An example of Fungi You know
Slide 6
Mushrooms – “Club Like” Fungi or Basidiomycete Fungi
Slide 7
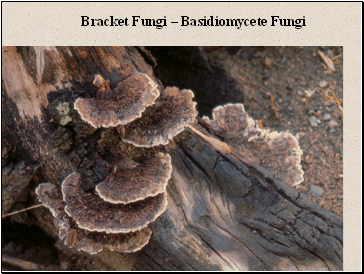
Bracket Fungi – Basidiomycete Fungi
Slide 8
Bread Mold – a Zygomycete Fungi
Slide 9
Cup Fungi – Ascomycete Fungi
Note the cup shapes and orange peel colour
Slide 10
Kingdom Fungi – you must know 5 Major Phyla
Phylum Zygomycota = the Bread Molds
Rhizopus – black bread mold
Oomycota = the Water Molds
Water mold, potato blight, mildew
Phylum Ascomycota = the Sac Fungi
Yeast, morels, truffles
Phylum Basidiomycota = the Club Fungi
Mushrooms, puffballs, bracket fungi, rusts, smuts, toadstools
Phylum Deuteromycota = the Fungi Imperfecti
Slide 11
Zygomycota (Rhizopus) the Common Molds
-are primarily decomposers
-asexual spores may be produced in sporangia
-sexual reproduction occurs between + and – strains forming a 2n zygote; a zygospore develops and may lie dormant for a long period of time; meiosis occurs just before germination
-only the zygote is diploid; all hyphae and asexual spores are haploid
Slide 12
Zygomycota – common molds
The fungal mass of hyphae, known as the MYCELIUM penetrates the bread and produces the fruiting bodies on top of the stalks
Mycelia = a mass of hyphae or filaments
Slide 13
Rhizoids = root-like hyphae
The zhizoids meet underground and mating occurs between hyphae of different molds (SEXUAL REPRODUCTION)
Slide 14
Contents
- Fungal Characteristics
- Zygomycota (Rhizopus) the Common Molds
- Zygomycota – common molds
- Ascomycota – Cup Fungi Life Cycle
- Yeast is an Ascomycete Fungus
- Life Cycle of Basidiomycete Fungi
- Other Basidiomycetes Rusts and Smuts
- Deuteromycota (Imperfect Fungi)
- Deuteromycota – the Fungi Imperfecti
- Water Molds -- Oomycota
- Things to Know about Oomycete Fungi
- Irish Potato Famine of 19th Century
- Cross Walls of Hyphae
- Lichens
- Mycorrhizae
Last added presentations
- Heat-Energy on the Move
- Newton’s Law of Gravity
- The Effects of Radiation on Living Things
- Space Radiation
- Thermal Energy
- Health Physics
- Simulation at NASA for the Space Radiation Effort